Page 100 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 100
FLOW MEASUREMENT 77
& Metal tube rotameters, which are also called, ar- the tip of the metering tube and at low flow rates
mored tube rotameters, in which indication is positions itself lower in the tube.
achieved by means of a magnet inside the float and & Some rotameters have spring loaded floats and there-
an external follower magnet linked to the pointer. No fore may be mounted in any orientation.
external electric power is involved.
. Illustrate how orifice meter–rotameter combination can
& Alternatively, armored (metal tube) rotameters can
be used to measure very high flow rates of liquids or
be set up with an electrical output taken off a con- gases.
verter. Then, metal tubes can be specified in applica- & Major disadvantages of the rotameter are its relative-
tions that require remote transmission of the mea-
ly high cost in larger sizes and the requirement that it
sured flow rate. This feature is not generally available
be installed vertically (there may not be enough head
with glass tube meters.
room).
. What are the temperature and pressure limits for glass
& The cost of a large rotameter installation can be
tube rotameters?
reduced by using an orifice bypass or a pitot tube in
& 120 C and 20 bar.
combination with a smaller rotameter.
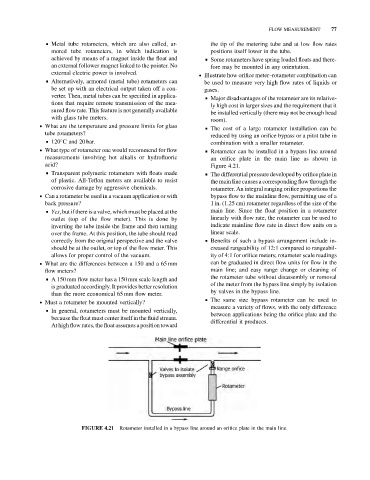
. What type of rotameter one would recommend for flow & Rotameter can be installed in a bypass line around
measurements involving hot alkalis or hydrofluoric an orifice plate in the main line as shown in
acid? Figure 4.21.
& Transparent polymeric rotameters with floats made & The differential pressure developed by orifice plate in
of plastic. All-Teflon meters are available to resist the main line causes a corresponding flow through the
corrosive damage by aggressive chemicals. rotameter. An integral ranging orifice proportions the
. Can a rotameter be used in a vacuum application or with bypass flow to the mainline flow, permitting use of a
back pressure? 1 in. (1.25 cm) rotameter regardless of the size of the
& Yes, butif there is a valve, which must be placed at the main line. Since the float position in a rotameter
outlet (top of the flow meter). This is done by linearly with flow rate, the rotameter can be used to
inverting the tube inside the frame and then turning indicate mainline flow rate in direct flow units on a
over the frame. At this position, the tube should read linear scale.
correctly from the original perspective and the valve & Benefits of such a bypass arrangement include in-
should be at the outlet, or top of the flow meter. This creased rangeability of 12:1 compared to rangeabil-
allows for proper control of the vacuum. ity of 4:1 for orifice meters; rotameter scale readings
. What are the differences between a 150 and a 65 mm can be graduated in direct flow units for flow in the
flow meters? main line; and easy range change or cleaning of
the rotameter tube without disassembly or removal
& A 150 mm flow meter has a 150 mm scale length and
of the meter from the bypass line simply by isolation
is graduated accordingly. It provides better resolution
by valves in the bypass line.
than the more economical 65 mm flow meter.
& The same size bypass rotameter can be used to
. Must a rotameter be mounted vertically?
measure a variety of flows, with the only difference
& In general, rotameters must be mounted vertically,
between applications being the orifice plate and the
because the float must center itself in the fluid stream.
differential it produces.
At high flow rates, the float assumes a position toward
Rotameter installed in a bypass line around an orifice plate in the main line.
FIGURE 4.21