Page 221 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 221
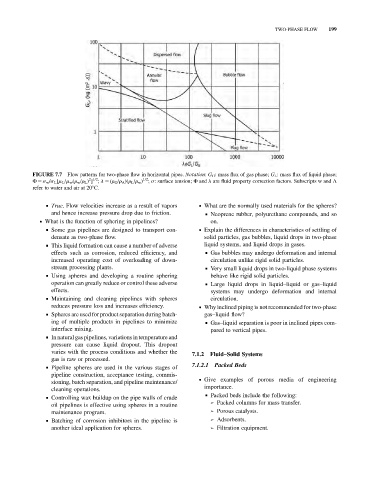
TWO-PHASE FLOW 199
FIGURE 7.7 Flow patterns for two-phase flow in horizontal pipes. Notation: G G : mass flux of gas phase; G L : mass flux of liquid phase;
1/2
2 1/2
F ¼ s w /s L [m L /m w (r w /r L ) ] ; l ¼ (r G /r A )(r L /r w ) ; s: surface tension; F and l are fluid property correction factors. Subscripts w and A
refer to water and air at 20 C.
& True. Flow velocities increase as a result of vapors . What are the normally used materials for the spheres?
and hence increase pressure drop due to friction. & Neoprene rubber, polyurethane compounds, and so
. What is the function of sphering in pipelines? on.
& Some gas pipelines are designed to transport con- . Explain the differences in characteristics of settling of
densate as two-phase flow. solid particles, gas bubbles, liquid drops in two-phase
& This liquid formation can cause a number of adverse liquid systems, and liquid drops in gases.
effects such as corrosion, reduced efficiency, and & Gas bubbles may undergo deformation and internal
increased operating cost of overloading of down- circulation unlike rigid solid particles.
stream processing plants. & Very small liquid drops in two-liquid phase systems
& Using spheres and developing a routine sphering behave like rigid solid particles.
operation can greatly reduce or control these adverse & Large liquid drops in liquid–liquid or gas–liquid
effects. systems may undergo deformation and internal
& Maintaining and cleaning pipelines with spheres circulation.
reduces pressure loss and increases efficiency. . Why inclined piping is not recommended for two-phase
& Spheres are used for product separation during batch- gas–liquid flow?
ing of multiple products in pipelines to minimize & Gas–liquid separation is poor in inclined pipes com-
interface mixing. pared to vertical pipes.
& In natural gas pipelines, variations in temperature and
pressure can cause liquid dropout. This dropout
varies with the process conditions and whether the
7.1.2 Fluid–Solid Systems
gas is raw or processed.
7.1.2.1 Packed Beds
& Pipeline spheres are used in the various stages of
pipeline construction, acceptance testing, commis-
. Give examples of porous media of engineering
sioning, batch separation, and pipeline maintenance/
importance.
cleaning operations.
& Packed beds include the following:
& Controlling wax buildup on the pipe walls of crude
oil pipelines is effective using spheres in a routine ➢ Packed columns for mass transfer.
maintenance program. ➢ Porous catalysts.
& Batching of corrosion inhibitors in the pipeline is ➢ Adsorbents.
another ideal application for spheres. ➢ Filtration equipment.