Page 226 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 226
204 TWO-PHASE FLOW SYSTEMS
& For N Fr < 1, particulate fluidization normally occurs,
and for N Fr > 1, aggregative fluidization takes place.
& For fluidization involving liquid–solid systems,
much lower values of Froude numbers are involved
because much lower values of minimum velocities
are involved for fluidization. Uniformity for fluidi-
zation in the case of liquids is much more compared
to gas-phase fluidization.
. How does pressure drop vary with velocity in fluid–
solid beds? Illustrate.
& As the superficial velocity approaches the minimum
fluidization velocity, V mf , the bed starts to expand,
and when the particles are no longer in physical
contact with one another, the bed is fluidized. DP
then becomes lower because of the increased voi-
dage, and consequently, the weight of particles per
unit height of bed is smaller. This drop continues until
the velocity is high enough for transport of the
material to take place and DP then starts to increase
again because the frictional drag of the fluid at the
walls of the pipe starts to become significant.
& Figure 7.11 illustrates the history of transformation
of pressure drop from fixed bed to fluidized bed
to pneumatic conveyance as superficial velocity
increases.
. Give the equation for minimum fluidization velocity.
3 2
V mf ¼ 0:0055½« =ð1 « mf Þd ðr rÞg=m; ð7:12Þ
mf s
where « mf is the void fraction.
& This equation is based on the Kozeny–Karman equa-
tion for pressure drop for fixed beds and is applicable
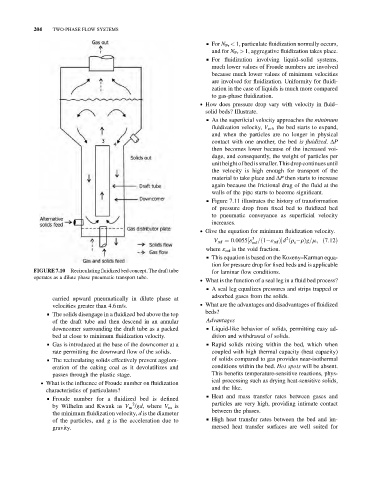
FIGURE 7.10 Recirculating fluidized bed concept. The draft tube for laminar flow conditions.
operates as a dilute phase pneumatic transport tube.
. What is the function of a seal leg in a fluid bed process?
& A seal leg equalizes pressures and strips trapped or
adsorbed gases from the solids.
carried upward pneumatically in dilute phase at
velocities greater than 4.6 m/s. . What are the advantages and disadvantages of fluidized
beds?
& The solids disengage in a fluidized bed above the top
of the draft tube and then descend in an annular Advantages
downcomer surrounding the draft tube as a packed & Liquid-like behavior of solids, permitting easy ad-
bed at close to minimum fluidization velocity. dition and withdrawal of solids.
& Gas is introduced at the base of the downcomer at a & Rapid solids mixing within the bed, which when
rate permitting the downward flow of the solids. coupled with high thermal capacity (heat capacity)
& The recirculating solids effectively prevent agglom- of solids compared to gas provides near-isothermal
eration of the caking coal as it devolatilizes and conditions within the bed. Hot spots will be absent.
passes through the plastic stage. This benefits temperature-sensitive reactions, phys-
ical processing such as drying heat-sensitive solids,
. What is the influence of Froude number on fluidization
and the like.
characteristics of particulates?
& Heat and mass transfer rates between gases and
& Froude number for a fluidized bed is defined
2
by Wilhelm and Kwauk as V m /gd,where V m is particles are very high, providing intimate contact
between the phases.
the minimum fluidization velocity, d is the diameter
of the particles, and g is the acceleration due to & High heat transfer rates between the bed and im-
gravity. mersed heat transfer surfaces are well suited for