Page 228 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 228
206 TWO-PHASE FLOW SYSTEMS
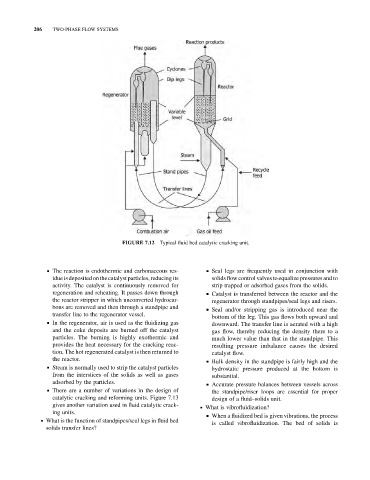
FIGURE 7.12 Typical fluid bed catalytic cracking unit.
& The reaction is endothermic and carbonaceous res- & Seal legs are frequently used in conjunction with
idue isdeposited onthe catalyst particles, reducing its solids flow control valves to equalize pressures and to
activity. The catalyst is continuously removed for strip trapped or adsorbed gases from the solids.
regeneration and reheating. It passes down through & Catalyst is transferred between the reactor and the
the reactor stripper in which unconverted hydrocar- regenerator through standpipes/seal legs and risers.
bons are removed and then through a standpipe and & Seal and/or stripping gas is introduced near the
transfer line to the regenerator vessel.
bottom of the leg. This gas flows both upward and
& In the regenerator, air is used as the fluidizing gas
downward. The transfer line is aerated with a high
and the coke deposits are burned off the catalyst gas flow, thereby reducing the density there to a
particles. The burning is highly exothermic and much lower value than that in the standpipe. This
provides the heat necessary for the cracking reac- resulting pressure imbalance causes the desired
tion. The hot regenerated catalyst is then returned to catalyst flow.
the reactor. & Bulk density in the standpipe is fairly high and the
& Steam is normally used to strip the catalyst particles
hydrostatic pressure produced at the bottom is
from the interstices of the solids as well as gases substantial.
adsorbed by the particles.
& Accurate pressure balances between vessels across
& There are a number of variations in the design of the standpipe/riser loops are essential for proper
catalytic cracking and reforming units. Figure 7.13 design of a fluid–solids unit.
gives another variation used in fluid catalytic crack- . What is vibrofluidization?
ing units.
& When a fluidized bed is given vibrations, the process
. What is the function of standpipes/seal legs in fluid bed
is called vibrofluidization. The bed of solids is
solids transfer lines?