Page 227 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 227
TWO-PHASE FLOW 205
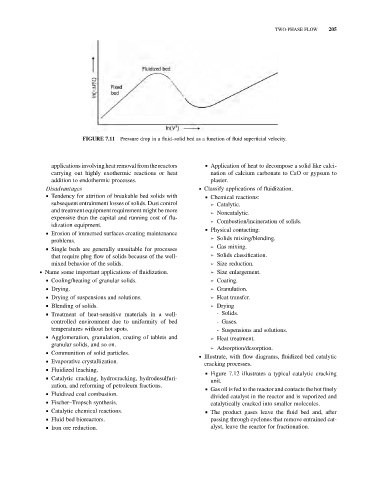
FIGURE 7.11 Pressure drop in a fluid–solid bed as a function of fluid superficial velocity.
applications involvingheat removal from the reactors & Application of heat to decompose a solid like calci-
carrying out highly exothermic reactions or heat nation of calcium carbonate to CaO or gypsum to
addition to endothermic processes. plaster.
Disadvantages . Classify applications of fluidization.
& Tendency for attrition of breakable bed solids with & Chemical reactions:
subsequent entrainment losses of solids. Dust control ➢ Catalytic.
and treatment equipment requirement might be more
➢ Noncatalytic.
expensive than the capital and running cost of flu-
➢ Combustion/incineration of solids.
idization equipment.
& Physical contacting:
& Erosion of immersed surfaces creating maintenance
➢ Solids mixing/blending.
problems.
➢ Gas mixing.
& Single beds are generally unsuitable for processes
that require plug flow of solids because of the well- ➢ Solids classification.
mixed behavior of the solids. ➢ Size reduction.
. Name some important applications of fluidization. ➢ Size enlargement.
& Cooling/heating of granular solids. ➢ Coating.
& Drying. ➢ Granulation.
& Drying of suspensions and solutions. ➢ Heat transfer.
& Blending of solids. ➢ Drying
& Treatment of heat-sensitive materials in a well- - Solids.
controlled environment due to uniformity of bed - Gases.
temperatures without hot spots. - Suspensions and solutions.
& Agglomeration, granulation, coating of tablets and ➢ Heat treatment.
granular solids, and so on.
➢ Adsorption/desorption.
& Communition of solid particles.
. Illustrate, with flow diagrams, fluidized bed catalytic
& Evaporative crystallization.
cracking processes.
& Fluidized leaching.
& Figure 7.12 illustrates a typical catalytic cracking
& Catalytic cracking, hydrocracking, hydrodesulfuri-
unit.
zation, and reforming of petroleum fractions.
& Gas oil is fed to the reactor and contacts the hot finely
& Fluidized coal combustion.
divided catalyst in the reactor and is vaporized and
& Fischer–Tropsch synthesis.
catalytically cracked into smaller molecules.
& Catalytic chemical reactions. & The product gases leave the fluid bed and, after
& Fluid bed bioreactors. passing through cyclones that remove entrained cat-
& Iron ore reduction. alyst, leave the reactor for fractionation.