Page 224 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 224
202 TWO-PHASE FLOW SYSTEMS
& Small particles are subject to electrostatic and inter- . What is a spouted bed?
particle forces, which increase nonuniformity in & Gas entering into solids at the conical base in the bed
fluidization. makes/drills a passage through the granular solids
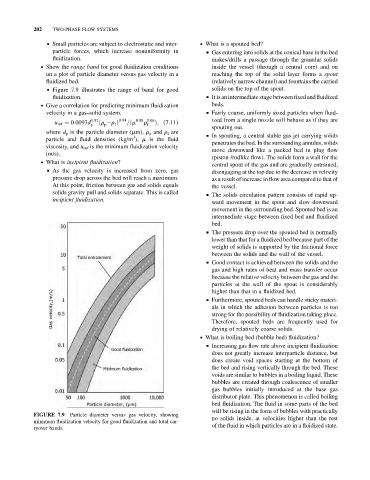
. Show the range band for good fluidization conditions inside the vessel (through a central core) and on
on a plot of particle diameter versus gas velocity in a reaching the top of the solid layer forms a spout
fluidized bed. (relatively narrow channel) and fountains the carried
& Figure 7.9 illustrates the range of band for good solids on the top of the spout.
fluidization. & It is an intermediate stage between fixed and fluidized
. Give a correlation for predicting minimum fluidization beds.
velocity in a gas–solid system. & Fairly coarse, uniformly sized particles when fluid-
r
u mf ¼ 0:0093d 1:82 ðr r Þ 0:94 =ðm 0:88 0:06 Þ; ð7:11Þ ized from a single nozzle will behave as if they are
p p f f
spouting out.
where d p is the particle diameter (mm), r p and r f are & In spouting, a central stable gas jet carrying solids
3
particle and fluid densities (kg/m ), m is the fluid
penetrates the bed. In the surrounding annulus, solids
viscosity, and u mf is the minimum fluidization velocity
move downward like a packed bed in plug flow
(m/s).
(piston-/rodlike flow). The solids form a wall for the
. What is incipient fluidization?
central spout of the gas and are gradually entrained,
& As the gas velocity is increased from zero, gas
disengaging at the top due to the decrease in velocity
pressure drop across the bed will reach a maximum. as a result of increase in flow area compared to that of
At this point, friction between gas and solids equals the vessel.
solids gravity pull and solids separate. This is called & The solids circulation pattern consists of rapid up-
incipient fluidization.
ward movement in the spout and slow downward
movement in the surrounding bed. Spouted bed is an
intermediate stage between fixed bed and fluidized
bed.
& The pressure drop over the spouted bed is normally
lower than that for a fluidized bed because part of the
weight of solids is supported by the frictional force
between the solids and the wall of the vessel.
& Good contact is achieved between the solids and the
gas and high rates of heat and mass transfer occur
because the relative velocity between the gas and the
particles at the wall of the spout is considerably
higher than that in a fluidized bed.
& Furthermore, spouted beds can handle sticky materi-
als in which the adhesion between particles is too
strong for the possibility of fluidization taking place.
Therefore, spouted beds are frequently used for
drying of relatively coarse solids.
. What is boiling bed (bubble bed) fluidization?
& Increasing gas flow rate above incipient fluidization
does not greatly increase interparticle distance, but
does create void spaces starting at the bottom of
the bed and rising vertically through the bed. These
voids are similar to bubbles in a boiling liquid. These
bubbles are created through coalescence of smaller
gas bubbles initially introduced at the base gas
distributor plate. This phenomenon is called boiling
bed fluidization. The fluid in some parts of the bed
will be rising in the form of bubbles with practically
FIGURE 7.9 Particle diameter versus gas velocity, showing
no solids inside, at velocities higher than the rest
minimum fluidization velocity for good fluidization and total car-
of the fluid in which particles are in a fluidized state.
ryover bands.