Page 88 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 88
FLOW MEASUREMENT 65
& Concentric orifices are, however, preferred for mul- & Used for liquid metering with entrained gas in small
tiphase flows in vertical lines because accumulation quantities.
of material is less likely and the sizing data for these Other Types:
plates is more reliable.
. Quadrant edge plate:
& The concentric orifice plate has a sharp (square-
& The quarter-circle orifice or the quadrant orifice is
edged) concentric bore that provides an almost pure
used for fluids of high viscosity. The orifice incor-
line contact between the plate and the fluid, with
porates a rounded edge of definite radius, which is a
negligible friction drag at the boundary.
particular function of the orifice diameter.
& The b-ratios of concentric orifice plates range from
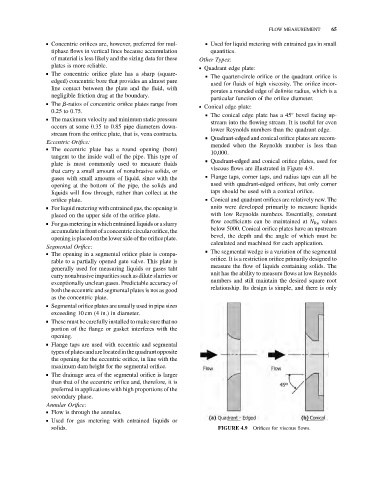
. Conical edge plate:
0.25 to 0.75.
& The conical edge plate has a 45 bevel facing up-
& The maximum velocity and minimum static pressure
stream into the flowing stream. It is useful for even
occurs at some 0.35 to 0.85 pipe diameters down-
lower Reynolds numbers than the quadrant edge.
stream from the orifice plate, that is, vena contracta.
& Quadrant-edged and conical orifice plates are recom-
Eccentric Orifice:
mended when the Reynolds number is less than
& The eccentric plate has a round opening (bore)
10,000.
tangent to the inside wall of the pipe. This type of
& Quadrant-edged and conical orifice plates, used for
plate is most commonly used to measure fluids
viscous flows are illustrated in Figure 4.9.
that carry a small amount of nonabrasive solids, or
gases with small amounts of liquid, since with the & Flange taps, corner taps, and radius taps can all be
opening at the bottom of the pipe, the solids and used with quadrant-edged orifices, but only corner
liquids will flow through, rather than collect at the taps should be used with a conical orifice.
orifice plate. & Conical and quadrant orifices are relatively new. The
& For liquid metering with entrained gas, the opening is units were developed primarily to measure liquids
placed on the upper side of the orifice plate. with low Reynolds numbers. Essentially, constant
flow coefficients can be maintained at N Re values
& Forgasmeteringinwhichentrained liquidsoraslurry
below 5000. Conical orifice plates have an upstream
accumulateinfrontofaconcentriccircularorifice,the
bevel, the depth and the angle of which must be
openingisplacedonthelowersideoftheorificeplate.
calculated and machined for each application.
Segmental Orifice:
& The segmental wedge is a variation of the segmental
& The opening in a segmental orifice plate is compa-
orifice. It is a restriction orifice primarily designed to
rable to a partially opened gate valve. This plate is
measure the flow of liquids containing solids. The
generally used for measuring liquids or gases taht
unit has the ability to measure flows at low Reynolds
carry nonabrasive impurities such as dilute slurries or
numbers and still maintain the desired square root
exceptionally unclean gases. Predictable accuracy of
relationship. Its design is simple, and there is only
both the eccentric and segmental plates is not as good
as the concentric plate.
& Segmental orifice plates are usually used in pipe sizes
exceeding 10 cm (4 in.) in diameter.
& These must be carefully installed to make sure that no
portion of the flange or gasket interferes with the
opening.
& Flange taps are used with eccentric and segmental
typesofplatesandarelocatedinthequadrantopposite
the opening for the eccentric orifice, in line with the
maximum dam height for the segmental orifice.
& The drainage area of the segmental orifice is larger
than that of the eccentric orifice and, therefore, it is
preferred in applications with high proportions of the
secondary phase.
Annular Orifice:
& Flow is through the annulus.
& Used for gas metering with entrained liquids or
solids. FIGURE 4.9 Orifices for viscous flows.