Page 127 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 127
Compressor Best Practices Be st Practice 3.1
piped to the second stage. The discharge from the second
stage enters an intercooler, and then it is piped to the third
stage.
Axial horizontal split
A typical axial compressor is shown in Figure 3.1.15.Anaxial
compressor consists of a rotor shaft with a series of rotating
blades, and a tapered cylindrical casing with fixed stator vanes.
Each set of blades is followed by a set of stator vanes. The gas
enters the inlet nozzle, which guides it to the inlet volute. The
inletvoluteguidesand acceleratesthe gasstream intothe
stator vanes. The stator vanes turn the gas stream to properly
align the gas with the blades. The blades increase the energy
of the gas by increasing its velocity. The stator vanes act as
diffusers to provide resistance to the gas flow, and they cause
Fig 3.1.8 Centrifugal compressor
the gas stream to decrease in velocity and to increase in
pressure. Since blades and stator vanes alternate down the
reduces the velocity of the gas as it leaves the impeller. The length of the casing, the gas is accelerated then decelerated
gas exits the diffuser through a volute casing, which collects several times before it leaves the compressor. Pressure is in-
the gas, further reduces its velocity, and recovers additional creased each time the gas flow meets a set of stator vanes. The
velocity energy. The gas exits the first stage through the first gas exits the compressor through the discharge volute and
stage discharge nozzle, enters an intercooler, and is then discharge nozzle.
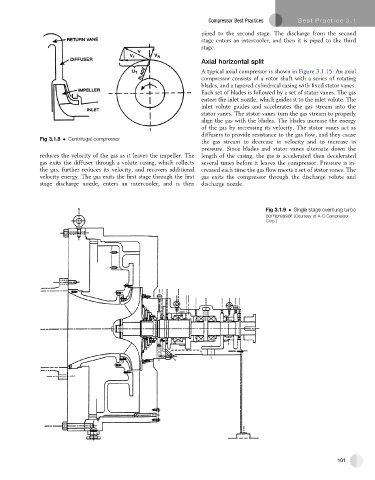
Fig 3.1.9 Single stage overhung turbo
compressor (Courtesy of A-C Compressor
Corp.)
101