Page 88 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 88
Be st Practice 2 .12 Pump Best Practices
Internal inlet pressure losses Cavitation is the result of released energy when an increase of
Formation of low pressure cells at low flows pressure surrounding the fluid causes the saturated vapor to change
Liquid temperature rise at low flows back to a liquid
Fig 2.12.12 Causes of vaporization within a centrifugal pump Fig 2.12.13 Cavitation definition
When operating at low flows, the efficiency of the impeller is
significantly reduced, thus increasing the liquid temperature rise. This indicates that vapor must be present before cavitation
As previously mentioned, the vapor pressure of any liquid in- can take place. The sources of vapor formation were discussed
creases with temperature. Increased temperature can cause the and are summarized in Figure 2.12.12. Referring back to
liquid to vaporize at the impeller vanes. Referring to Figure 2.12.8, it can be seen that as soon as the liquid enters the
impeller vane area, its energy and pressure rapidly increase.
Figure 2.12.12, it can be seen that low specific gravity liquids with
high vapor pressures are the most susceptible to vaporization When its pressure liquid exceeds the vapor pressure, the vapor
bubbles will collapse and cavitation will occur. Ways to prevent
caused by low flow operation. Note that increased wear ring
clearances can worsen this situation, since the higher temperature cavitation are shown in Figure 2.12.14. They will be discussed in
liquid will mix with the cooler liquid entering the impeller. more details later on in this chapter.
Figure 2.12.12 summarizes the causes of vaporization within a
centrifugal pump.
Cavitation is prevented by preventing vapor formation within a pump
Causes of damage
Fig 2.12.14 Preventing cavitation
In the above section the causes of vapor formation within
a pump were described. In this section the causes of damage to
pump components will be discussed. The effects of fluids on component damage
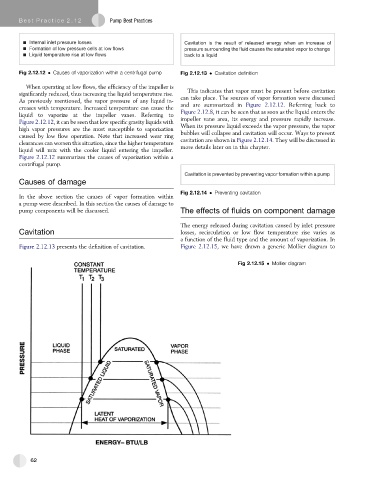
The energy released during cavitation caused by inlet pressure
Cavitation losses, recirculation or low flow temperature rise varies as
a function of the fluid type and the amount of vaporization. In
Figure 2.12.13 presents the definition of cavitation. Figure 2.12.15, we have drawn a generic Mollier diagram to
Fig 2.12.15 Mollier diagram
62