Page 96 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 96
Be st Practice 2 .13 Pump Best Practices
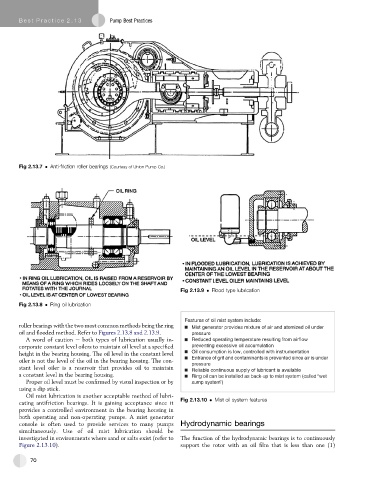
Fig 2.13.7 Anti-friction roller bearings (Courtesy of Union Pump Co.)
Fig 2.13.9 Flood type lubrication
Fig 2.13.8 Ring oil lubrication
Features of oil mist system include:
roller bearings with the two most common methods being the ring Mist generator provides mixture of air and atomized oil under
oil and flooded method. Refer to Figures 2.13.8 and 2.13.9. pressure
A word of caution e both types of lubrication usually in- Reduced operating temperature resulting from airflow
corporate constant level oilers to maintain oil level at a specified preventing excessive oil accumulation
height in the bearing housing. The oil level in the constant level Oil consumption is low, controlled with instrumentation
oiler is not the level of the oil in the bearing housing. The con- Entrance of grit and contaminants is prevented since air is under
pressure
stant level oiler is a reservoir that provides oil to maintain
Reliable continuous supply of lubricant is available
a constant level in the bearing housing. Ring oil can be installed as back-up to mist system (called “wet
Proper oil level must be confirmed by visual inspection or by sump system”)
using a dip stick.
Oil mist lubrication is another acceptable method of lubri-
cating antifriction bearings. It is gaining acceptance since it Fig 2.13.10 Mist oil system features
provides a controlled environment in the bearing housing in
both operating and non-operating pumps. A mist generator
console is often used to provide services to many pumps Hydrodynamic bearings
simultaneously. Use of oil mist lubrication should be
investigated in environments where sand or salts exist (refer to The function of the hydrodynamic bearings is to continuously
Figure 2.13.10). support the rotor with an oil film that is less than one (1)
70