Page 323 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 323
Internet of things for smart grid applications Chapter 7 287
smart grid applications. Many novel communication technologies including
LPWAN, UMTS, LTE, LTE-A, and narrow band IoT (NB-IoT) have been
emerged in addition to BLE in Personal Area Networks and Zigbee in the
use of HEMS. The improved technologies provided long-range communication
in the unlicensed bands for IoT and smart grid applications. The most prominent
LPWAN technologies are known with the names of Ultra Narrow Band (UNB)
by SIGFOX, LoRa by Semtech, LTE machine-type communications (LTE-M),
and NB-IoT. The comparisons of well-known communication methods have
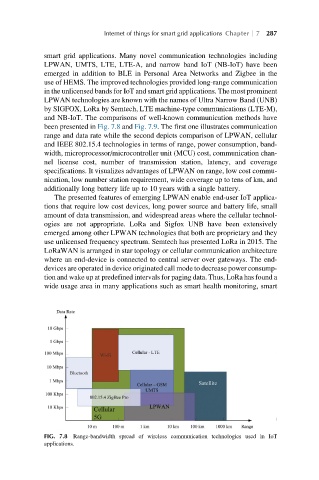
been presented in Fig. 7.8 and Fig. 7.9. The first one illustrates communication
range and data rate while the second depicts comparison of LPWAN, cellular
and IEEE 802.15.4 technologies in terms of range, power consumption, band-
width, microprocessor/microcontroller unit (MCU) cost, communication chan-
nel license cost, number of transmission station, latency, and coverage
specifications. It visualizes advantages of LPWAN on range, low cost commu-
nication, low number station requirement, wide coverage up to tens of km, and
additionally long battery life up to 10 years with a single battery.
The presented features of emerging LPWAN enable end-user IoT applica-
tions that require low cost devices, long power source and battery life, small
amount of data transmission, and widespread areas where the cellular technol-
ogies are not appropriate. LoRa and Sigfox UNB have been extensively
emerged among other LPWAN technologies that both are proprietary and they
use unlicensed frequency spectrum. Semtech has presented LoRa in 2015. The
LoRaWAN is arranged in star topology or cellular communication architecture
where an end-device is connected to central server over gateways. The end-
devices are operated in device originated call mode to decrease power consump-
tion and wake up at predefined intervals for paging data. Thus, LoRa has found a
wide usage area in many applications such as smart health monitoring, smart
FIG. 7.8 Range-bandwidth spread of wireless communication technologies used in IoT
applications.