Page 234 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution 3E
P. 234
I. Analysis and Measurement of Gaseous Pollutants 197
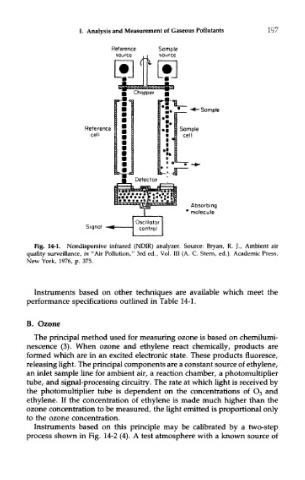
Fig. 14-1. Nondispersive infrared (NDIR) analyzer. Source: Bryan, R. }., Ambient air
quality surveillance, in "Air Pollution," 3rd ed., Vol. Ill (A. C. Stern, ed.). Academic Press,
New York, 1976, p. 375.
Instruments based on other techniques are available which meet the
performance specifications outlined in Table 14-1.
B. Ozone
The principal method used for measuring ozone is based on chemilumi-
nescence (3). When ozone and ethylene react chemically, products are
formed which are in an excited electronic state. These products fluoresce,
releasing light. The principal components are a constant source of ethylene,
an inlet sample line for ambient air, a reaction chamber, a photomultiplier
tube, and signal-processing circuitry. The rate at which light is received by
the photomultiplier tube is dependent on the concentrations of O 3 and
ethylene. If the concentration of ethylene is made much higher than the
ozone concentration to be measured, the light emitted is proportional only
to the ozone concentration.
Instruments based on this principle may be calibrated by a two-step
process shown in Fig. 14-2 (4). A test atmosphere with a known source of