Page 236 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution 3E
P. 236
I. Analysis and Measurement of Gaseous Pollutants 199
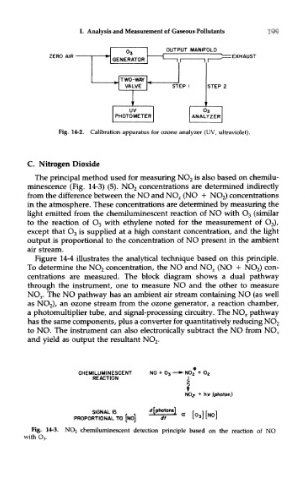
Fig. 14-2. Calibration apparatus for ozone analyzer (UV, ultraviolet).
C. Nitrogen Dioxide
The principal method used for measuring NO 2 is also based on chemilu-
minescence (Fig. 14-3) (5). NO 2 concentrations are determined indirectly
from the difference between the NO and NO X (NO + NO 2) concentrations
in the atmosphere. These concentrations are determined by measuring the
light emitted from the chemiluminescent reaction of NO with O 3 (similar
to the reaction of O 3 with ethylene noted for the measurement of O 3),
except that O 3 is supplied at a high constant concentration, and the light
output is proportional to the concentration of NO present in the ambient
air stream.
Figure 14-4 illustrates the analytical technique based on this principle.
To determine the NO 2 concentration, the NO and NO X (NO + NO 2) con-
centrations are measured. The block diagram shows a dual pathway
through the instrument, one to measure NO and the other to measure
NO.,.. The NO pathway has an ambient air stream containing NO (as well
as NO 2), an ozone stream from the ozone generator, a reaction chamber,
a photomultiplier tube, and signal-processing circuitry. The NO X pathway
has the same components, plus a converter for quantitatively reducing NO 2
to NO. The instrument can also electronically subtract the NO from NO T
and yield as output the resultant NO 2.
Fig. 14-3. NO 2 chemiluminescent detection principle based on the reaction of NO
with O 3.