Page 265 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution
P. 265
226 15. Air Pollution Monitoring and Surveillance
The external audit results are used to determine the accuracy of the measure-
ments. Accuracy is calculated from percentage differences, d ir for the audit
concentrations and the instrument response.
V. DATA ANALYSIS AND DISPLAY
In general, air quality data are classified as a function of time, location,
and magnitude. Several statistical parameters may be used to characterize
a group of air pollution concentrations, including the arithmetic mean, the
median, and the geometric mean. These parameters may be determined
over averaging times of up to 1 year. In addition to these three parameters,
a measure of the variability of a data set, such as the standard deviation
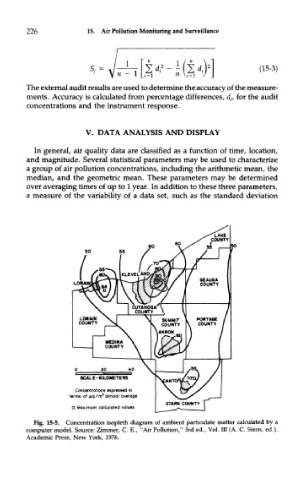
Fig. 15-5. Concentration isopleth diagram of ambient particulate matter calculated by a
computer model. Source: Zimmer, C. E., "Air Pollution," 3rd ed., Vol. Ill (A. C. Stern, ed.).
Academic Press, New York, 1976.