Page 84 - Fundamentals of Communications Systems
P. 84
2.36 Chapter Two
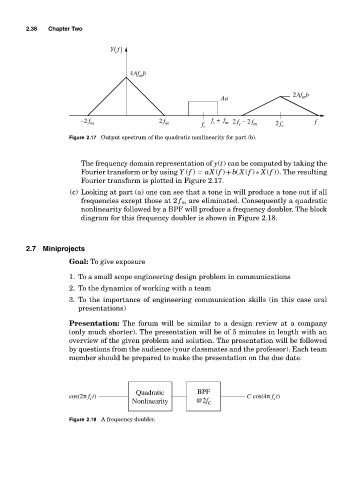
Yf ()
4Af b
m
2Af b
m
Aa
−2 f m 2 f m f c f + f m 2 f c − 2 f m 2 f c f
c
Figure 2.17 Output spectrum of the quadratic nonlinearity for part (b).
The frequency domain representation of y(t) can be computed by taking the
Fourier transform or by using Y (f ) = aX(f )+b(X(f )∗ X(f )). The resulting
Fourier transform is plotted in Figure 2.17.
(c) Looking at part (a) one can see that a tone in will produce a tone out if all
frequencies except those at 2 f m are eliminated. Consequently a quadratic
nonlinearity followed by a BPF will produce a frequency doubler. The block
diagram for this frequency doubler is shown in Figure 2.18.
2.7 Miniprojects
Goal: To give exposure
1. To a small scope engineering design problem in communications
2. To the dynamics of working with a team
3. To the importance of engineering communication skills (in this case oral
presentations)
Presentation: The forum will be similar to a design review at a company
(only much shorter). The presentation will be of 5 minutes in length with an
overview of the given problem and solution. The presentation will be followed
by questions from the audience (your classmates and the professor). Each team
member should be prepared to make the presentation on the due date.
Quadratic BPF
cos(2π f t) C cos(4π f t)
c c
Nonlinearity @2f c
Figure 2.18 A frequency doubler.