Page 150 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 150
SMALL-SCALE TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL LANDFORMS 133
Box 5.1
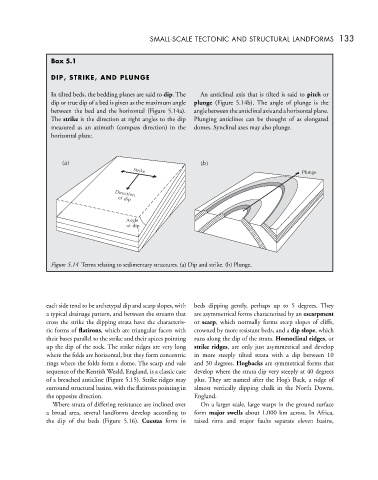
DIP, STRIKE, AND PLUNGE
In tilted beds, the bedding planes are said to dip. The An anticlinal axis that is tilted is said to pitch or
dip or true dip of a bed is given as the maximum angle plunge (Figure 5.14b). The angle of plunge is the
between the bed and the horizontal (Figure 5.14a). angle between the anticlinal axis and a horizontal plane.
The strike is the direction at right angles to the dip Plunging anticlines can be thought of as elongated
measured as an azimuth (compass direction) in the domes. Synclinal axes may also plunge.
horizontal plane.
a
() ()
b
Strike
Plunge
Direction
of dip
Angle
of dip
Figure 5.14 Terms relating to sedimentary structures. (a) Dip and strike. (b) Plunge.
each side tend to be archetypal dip and scarp slopes, with beds dipping gently, perhaps up to 5 degrees. They
a typical drainage pattern, and between the streams that are asymmetrical forms characterized by an escarpment
cross the strike the dipping strata have the characteris- or scarp, which normally forms steep slopes of cliffs,
tic forms of flatirons, which are triangular facets with crowned by more resistant beds, and a dip slope, which
their bases parallel to the strike and their apices pointing runs along the dip of the strata. Homoclinal ridges,or
up the dip of the rock. The strike ridges are very long strike ridges, are only just asymmetrical and develop
where the folds are horizontal, but they form concentric in more steeply tilted strata with a dip between 10
rings where the folds form a dome. The scarp and vale and 30 degrees. Hogbacks are symmetrical forms that
sequence of the Kentish Weald, England, is a classic case develop where the strata dip very steeply at 40 degrees
of a breached anticline (Figure 5.15). Strike ridges may plus. They are named after the Hog’s Back, a ridge of
surround structural basins, with the flatirons pointing in almost vertically dipping chalk in the North Downs,
the opposite direction. England.
Where strata of differing resistance are inclined over On a larger scale, large warps in the ground surface
a broad area, several landforms develop according to form major swells about 1,000 km across. In Africa,
the dip of the beds (Figure 5.16). Cuestas form in raised rims and major faults separate eleven basins,