Page 149 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 149
132 STRUCTURE
isolated tower, a jagged peak, or a rounded hill, depend- from other directions. Domes are also termed periclines.
ing on the caprock thickness. In stepped topography, An example is the Chaldon pericline in Dorset, England,
scarps display a sequence of structural benches, produced in which rings of progressively younger rocks – Wealden
by harder beds, and steep bluffs where softer beds have Beds, Upper Greensand, and Chalk – outcrop around
been eaten away (see Colour Plate 10, inserted between a core of Upper Jurassic Portland and Purbeck beds.
pages 208 and 209). Domed structures also form where the crust is thrust
upwards, although these forms are usually simpler than
Folded beds those formed by more complex pressure distributions.
Domes are found, too, where plugs of light material,
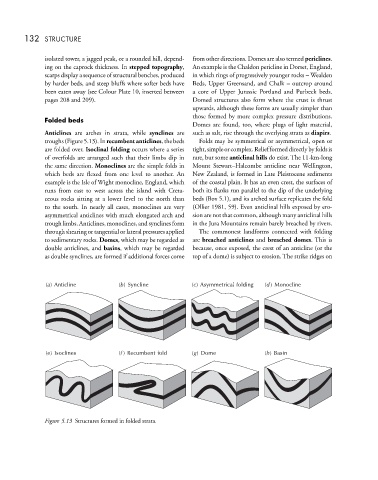
Anticlines are arches in strata, while synclines are such as salt, rise through the overlying strata as diapirs.
troughs (Figure 5.13). In recumbent anticlines, the beds Folds may be symmetrical or asymmetrical, open or
are folded over. Isoclinal folding occurs where a series tight,simpleorcomplex.Reliefformeddirectlybyfoldsis
of overfolds are arranged such that their limbs dip in rare, but some anticlinal hills do exist. The 11-km-long
the same direction. Monoclines are the simple folds in Mount Stewart–Halcombe anticline near Wellington,
which beds are flexed from one level to another. An New Zealand, is formed in Late Pleistocene sediments
example is the Isle of Wight monocline, England, which of the coastal plain. It has an even crest, the surfaces of
runs from east to west across the island with Creta- both its flanks run parallel to the dip of the underlying
ceous rocks sitting at a lower level to the north than beds (Box 5.1), and its arched surface replicates the fold
to the south. In nearly all cases, monoclines are very (Ollier 1981, 59). Even anticlinal hills exposed by ero-
asymmetrical anticlines with much elongated arch and sion are not that common, although many anticlinal hills
trough limbs. Anticlines, monoclines, and synclines form in the Jura Mountains remain barely breached by rivers.
through shearing or tangential or lateral pressures applied The commonest landforms connected with folding
to sedimentary rocks. Domes, which may be regarded as are breached anticlines and breached domes. This is
double anticlines, and basins, which may be regarded because, once exposed, the crest of an anticline (or the
as double synclines, are formed if additional forces come top of a dome) is subject to erosion. The strike ridges on
b
c
d
() Anticline ( ) Syncline () Asymmetrical folding ( ) Monocline
a
h
g
( ) Isoclines ( ) Recumbent fold () Dome () Basin
e
f
Figure 5.13 Structures formed in folded strata.