Page 146 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 146
SMALL-SCALE TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL LANDFORMS 129
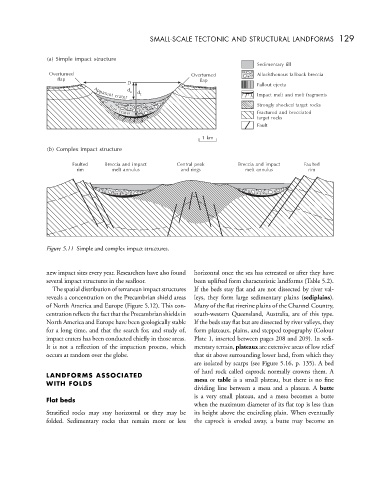
a
( ) Simple impact structure
Sedimentary fill
Overturned Overturned Allochthonous fallback breccia
flap flap
D
Fallout ejecta
d a
Impact melt and melt fragments
d t
Apparent crater
Strongly shocked target rocks
Fractured and brecciated
True crater
True crater
target rocks
Fault
1km
b
() Complex impact structure
Faulted Breccia and impact Central peak Breccia and impact Faulted
rim melt annulus and rings melt annulus rim
Figure 5.11 Simple and complex impact structures.
new impact sites every year. Researchers have also found horizontal once the sea has retreated or after they have
several impact structures in the seafloor. been uplifted form characteristic landforms (Table 5.2).
The spatial distribution of terranean impact structures If the beds stay flat and are not dissected by river val-
reveals a concentration on the Precambrian shield areas leys, they form large sedimentary plains (sediplains).
of North America and Europe (Figure 5.12). This con- Many of the flat riverine plains of the Channel Country,
centration reflects the fact that the Precambrian shields in south-western Queensland, Australia, are of this type.
North America and Europe have been geologically stable If the beds stay flat but are dissected by river valleys, they
for a long time, and that the search for, and study of, form plateaux, plains, and stepped topography (Colour
impact craters has been conducted chiefly in those areas. Plate 1, inserted between pages 208 and 209). In sedi-
It is not a reflection of the impaction process, which mentary terrain, plateaux are extensive areas of low relief
occurs at random over the globe. that sit above surrounding lower land, from which they
are isolated by scarps (see Figure 5.16, p. 135). A bed
of hard rock called caprock normally crowns them. A
LANDFORMS ASSOCIATED
WITH FOLDS mesa or table is a small plateau, but there is no fine
dividing line between a mesa and a plateau. A butte
is a very small plateau, and a mesa becomes a butte
Flat beds
when the maximum diameter of its flat top is less than
Stratified rocks may stay horizontal or they may be its height above the encircling plain. When eventually
folded. Sedimentary rocks that remain more or less the caprock is eroded away, a butte may become an