Page 148 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 148
SMALL-SCALE TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL LANDFORMS 131
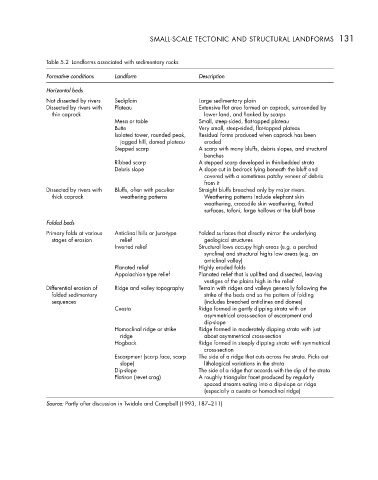
Table 5.2 Landforms associated with sedimentary rocks
Formative conditions Landform Description
Horizontal beds
Not dissected by rivers Sediplain Large sedimentary plain
Dissected by rivers with Plateau Extensive flat area formed on caprock, surrounded by
thin caprock lower land, and flanked by scarps
Mesa or table Small, steep-sided, flat-topped plateau
Butte Very small, steep-sided, flat-topped plateau
Isolated tower, rounded peak, Residual forms produced when caprock has been
jagged hill, domed plateau eroded
Stepped scarp A scarp with many bluffs, debris slopes, and structural
benches
Ribbed scarp A stepped scarp developed in thin-bedded strata
Debris slope A slope cut in bedrock lying beneath the bluff and
covered with a sometimes patchy veneer of debris
from it
Dissected by rivers with Bluffs, often with peculiar Straight bluffs breached only by major rivers.
thick caprock weathering patterns Weathering patterns include elephant skin
weathering, crocodile skin weathering, fretted
surfaces, tafoni, large hollows at the bluff base
Folded beds
Primary folds at various Anticlinal hills or Jura-type Folded surfaces that directly mirror the underlying
stages of erosion relief geological structures
Inverted relief Structural lows occupy high areas (e.g. a perched
syncline) and structural highs low areas (e.g. an
anticlinal valley)
Planated relief Highly eroded folds
Appalachian-type relief Planated relief that is uplifted and dissected, leaving
vestiges of the plains high in the relief
Differential erosion of Ridge and valley topography Terrain with ridges and valleys generally following the
folded sedimentary strike of the beds and so the pattern of folding
sequences (includes breached anticlines and domes)
Cuesta Ridge formed in gently dipping strata with an
asymmetrical cross-section of escarpment and
dip-slope
Homoclinal ridge or strike Ridge formed in moderately dipping strata with just
ridge about asymmetrical cross-section
Hogback Ridge formed in steeply dipping strata with symmetrical
cross-section
Escarpment (scarp face, scarp The side of a ridge that cuts across the strata. Picks out
slope) lithological variations in the strata
Dip-slope The side of a ridge that accords with the dip of the strata
Flatiron (revet crag) A roughly triangular facet produced by regularly
spaced streams eating into a dip-slope or ridge
(especially a cuesta or homoclinal ridge)
Source: Partly after discussion in Twidale and Campbell (1993, 187–211)