Page 60 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 60
THE GEOMORPHIC SYSTEM 43
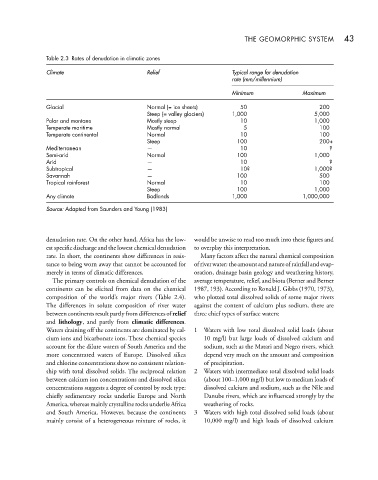
Table 2.3 Rates of denudation in climatic zones
Climate Relief Typical range for denudation
rate (mm/millennium)
Minimum Maximum
Glacial Normal (= ice sheets) 50 200
Steep (= valley glaciers) 1,000 5,000
Polar and montane Mostly steep 10 1,000
Temperate maritime Mostly normal 5 100
Temperate continental Normal 10 100
Steep 100 200+
Mediterranean — 10 ?
Semi-arid Normal 100 1,000
Arid — 10 ?
Subtropical — 10? 1,000?
Savannah — 100 500
Tropical rainforest Normal 10 100
Steep 100 1,000
Any climate Badlands 1,000 1,000,000
Source: Adapted from Saunders and Young (1983)
denudation rate. On the other hand, Africa has the low- would be unwise to read too much into these figures and
est specific discharge and the lowest chemical denudation to overplay this interpretation.
rate. In short, the continents show differences in resis- Many factors affect the natural chemical composition
tance to being worn away that cannot be accounted for ofriverwater:theamountandnatureofrainfallandevap-
merely in terms of climatic differences. oration, drainage basin geology and weathering history,
The primary controls on chemical denudation of the average temperature, relief, and biota (Berner and Berner
continents can be elicited from data on the chemical 1987, 193). According to Ronald J. Gibbs (1970, 1973),
composition of the world’s major rivers (Table 2.4). who plotted total dissolved solids of some major rivers
The differences in solute composition of river water against the content of calcium plus sodium, there are
between continents result partly from differences of relief three chief types of surface waters:
and lithology, and partly from climatic differences.
Waters draining off the continents are dominated by cal- 1 Waters with low total dissolved solid loads (about
cium ions and bicarbonate ions. These chemical species 10 mg/l) but large loads of dissolved calcium and
account for the dilute waters of South America and the sodium, such as the Matari and Negro rivers, which
more concentrated waters of Europe. Dissolved silica depend very much on the amount and composition
and chlorine concentrations show no consistent relation- of precipitation.
ship with total dissolved solids. The reciprocal relation 2 Waters with intermediate total dissolved solid loads
between calcium ion concentrations and dissolved silica (about 100–1,000 mg/l) but low to medium loads of
concentrations suggests a degree of control by rock type: dissolved calcium and sodium, such as the Nile and
chiefly sedimentary rocks underlie Europe and North Danube rivers, which are influenced strongly by the
America, whereas mainly crystalline rocks underlie Africa weathering of rocks.
and South America. However, because the continents 3 Waters with high total dissolved solid loads (about
mainly consist of a heterogeneous mixture of rocks, it 10,000 mg/l) and high loads of dissolved calcium