Page 159 - Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging
P. 159
142 POLARIZATION MICROSCOPY
Background
A
-plate
1 2 3 1 2 3
(a)
Object
A
-plate
object
1 2 3
1 2 3
(b)
Object
A
-plate
object
1 2 3
1 2 3
(c)
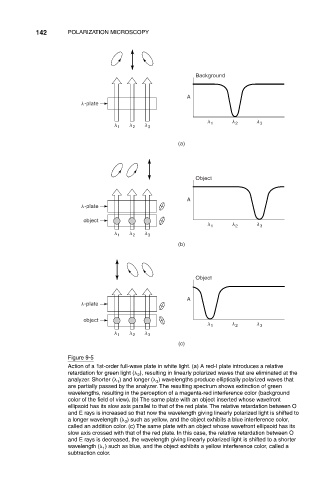
Figure 9-5
Action of a 1st-order full-wave plate in white light. (a) A red-I plate introduces a relative
retardation for green light ( ), resulting in linearly polarized waves that are eliminated at the
2
analyzer. Shorter ( ) and longer ( ) wavelengths produce elliptically polarized waves that
3
1
are partially passed by the analyzer. The resulting spectrum shows extinction of green
wavelengths, resulting in the perception of a magenta-red interference color (background
color of the field of view). (b) The same plate with an object inserted whose wavefront
ellipsoid has its slow axis parallel to that of the red plate. The relative retardation between O
and E rays is increased so that now the wavelength giving linearly polarized light is shifted to
a longer wavelength ( ) such as yellow, and the object exhibits a blue interference color,
3
called an addition color. (c) The same plate with an object whose wavefront ellipsoid has its
slow axis crossed with that of the red plate. In this case, the relative retardation between O
and E rays is decreased, the wavelength giving linearly polarized light is shifted to a shorter
wavelength ( ) such as blue, and the object exhibits a yellow interference color, called a
1
subtraction color.