Page 90 - Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging
P. 90
DIFFRACTION BY A GRATING AND CALCULATION OF ITS LINE SPACING, D 73
2
1
2
Grating
1
0
Screen
–1
(a)
2
2
1
2
1
0
1
2
d
2 0
1
0
1
(b)
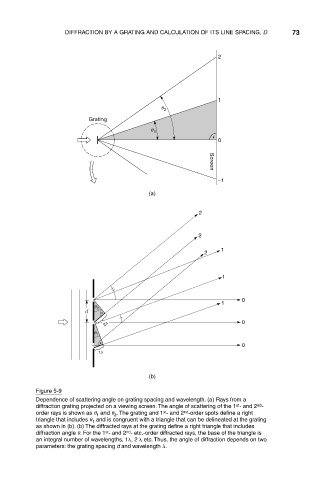
Figure 5-9
Dependence of scattering angle on grating spacing and wavelength. (a) Rays from a
st
nd
diffraction grating projected on a viewing screen. The angle of scattering of the 1 - and 2 -
nd
st
order rays is shown as and . The grating and 1 - and 2 -order spots define a right
2
1
triangle that includes and is congruent with a triangle that can be delineated at the grating
1
as shown in (b). (b) The diffracted rays at the grating define a right triangle that includes
diffraction angle . For the 1 - and 2 - etc.-order diffracted rays, the base of the triangle is
st
nd
an integral number of wavelengths, 1 , 2 etc. Thus, the angle of diffraction depends on two
parameters: the grating spacing d and wavelength .