Page 425 - Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
P. 425
Safety of Fusion Reactors Chapter | 14 403
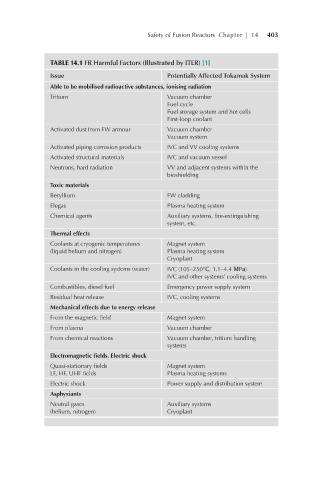
TABLE 14.1 FR Harmful Factors (Illustrated by ITER) [1]
Issue Potentially Affected Tokamak System
Able to be mobilised radioactive substances, ionising radiation
Tritium Vacuum chamber
Fuel cycle
Fuel storage system and hot cells
First-loop coolant
Activated dust from FW armour Vacuum chamber
Vacuum system
Activated piping corrosion products IVC and VV cooling systems
Activated structural materials IVC and vacuum vessel
Neutrons, hard radiation VV and adjacent systems within the
bioshielding
Toxic materials
Beryllium FW cladding
Elegas Plasma heating system
Chemical agents Auxiliary systems, fire-extinguishing
system, etc.
Thermal effects
Coolants at cryogenic temperatures Magnet system
(liquid helium and nitrogen) Plasma heating system
Cryoplant
Coolants in the cooling systems (water) IVC (105–250°С, 1.1–4.4 МPа)
IVC and other systems’ cooling systems
Combustibles, diesel fuel Emergency power supply system
Residual heat release IVC, cooling systems
Mechanical effects due to energy release
From the magnetic field Magnet system
From plasma Vacuum chamber
From chemical reactions Vacuum chamber, tritium handling
systems
Electromagnetic fields. Electric shock
Quasi-stationary fields Magnet system
LF, HF, UHF fields Plasma heating systems
Electric shock Power supply and distribution system
Asphyxiants
Neutral gases Auxiliary systems
(helium, nitrogen) Cryoplant