Page 142 - Fundamentals of Ocean Renewable Energy Generating Electricity From The Sea
P. 142
Wave Energy Chapter | 5 133
F ext
Incident wave Radiating wave
Float
Still water level
F rad
F res
F PTO
Added mass
Power take-off unit
z
Sea bed
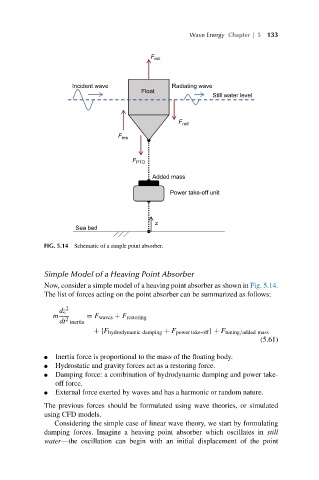
FIG. 5.14 Schematic of a simple point absorber.
Simple Model of a Heaving Point Absorber
Now, consider a simple model of a heaving point absorber as shown in Fig. 5.14.
The list of forces acting on the point absorber can be summarized as follows:
dz 2
m = F waves + F restoring
2
dt inertia
+{F hydrodynamic damping + F power take-off }+ F tuning/added mass
(5.61)
● Inertia force is proportional to the mass of the floating body.
● Hydrostatic and gravity forces act as a restoring force.
● Damping force: a combination of hydrodynamic damping and power take-
off force.
● External force exerted by waves and has a harmonic or random nature.
The previous forces should be formulated using wave theories, or simulated
using CFD models.
Considering the simple case of linear wave theory, we start by formulating
damping forces. Imagine a heaving point absorber which oscillates in still
water—the oscillation can begin with an initial displacement of the point