Page 76 - Fundamentals of Ocean Renewable Energy Generating Electricity From The Sea
P. 76
68 Fundamentals of Ocean Renewable Energy
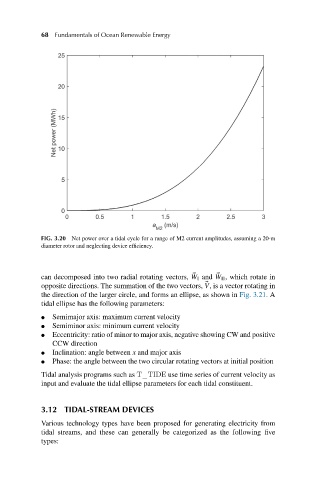
FIG. 3.20 Net power over a tidal cycle for a range of M2 current amplitudes, assuming a 20-m
diameter rotor and neglecting device efficiency.
can decomposed into two radial rotating vectors, W I and W II , which rotate in
opposite directions. The summation of the two vectors, V, is a vector rotating in
the direction of the larger circle, and forms an ellipse, as shown in Fig. 3.21. A
tidal ellipse has the following parameters:
● Semimajor axis: maximum current velocity
● Semiminor axis: minimum current velocity
● Eccentricity: ratio of minor to major axis, negative showing CW and positive
CCW direction
● Inclination: angle between x and major axis
● Phase: the angle between the two circular rotating vectors at initial position
Tidal analysis programs such as T_TIDE use time series of current velocity as
input and evaluate the tidal ellipse parameters for each tidal constituent.
3.12 TIDAL-STREAM DEVICES
Various technology types have been proposed for generating electricity from
tidal streams, and these can generally be categorized as the following five
types: