Page 70 - Fundamentals of Physical Volcanology
P. 70
9780632054435_4_004.qxd 12/10/2007 12:19PM Page 47
MAGMA STORAGE 47
(a)
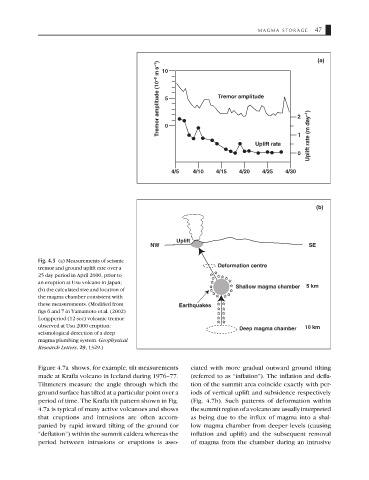
Tremor amplitude (10 –8 m s –1 ) 5 Tremor amplitude 2
10
0
Uplift rate 1 Uplift rate (m day –1 )
0
4/5 4/10 4/15 4/20 4/25 4/30
(b)
Uplift
NW SE
Fig. 4.5 (a) Measurements of seismic
Deformation centre
tremor and ground uplift rate over a
25 day period in April 2000, prior to
an eruption at Usu volcano in Japan;
Shallow magma chamber 5 km
(b) the calculated size and location of
the magma chamber consistent with
these measurements. (Modified from Earthquakes
figs 6 and 7 in Yamamoto et al. (2002)
Long-period (12 sec) volcanic tremor
observed at Usu 2000 eruption: 10 km
Deep magma chamber
seismological detection of a deep
magma plumbing system. Geophysical
Research Letters, 29, 1329.)
Figure 4.7a shows, for example, tilt measurements ciated with more gradual outward ground tilting
made at Krafla volcano in Iceland during 1976–77. (referred to as “inflation”). The inflation and defla-
Tiltmeters measure the angle through which the tion of the summit area coincide exactly with per-
ground surface has tilted at a particular point over a iods of vertical uplift and subsidence respectively
period of time. The Krafla tilt pattern shown in Fig. (Fig. 4.7b). Such patterns of deformation within
4.7a is typical of many active volcanoes and shows the summit region of a volcano are usually interpreted
that eruptions and intrusions are often accom- as being due to the influx of magma into a shal-
panied by rapid inward tilting of the ground (or low magma chamber from deeper levels (causing
“deflation”) within the summit caldera whereas the inflation and uplift) and the subsequent removal
period between intrusions or eruptions is asso- of magma from the chamber during an intrusive