Page 48 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 48
Basic Probability Concepts 31
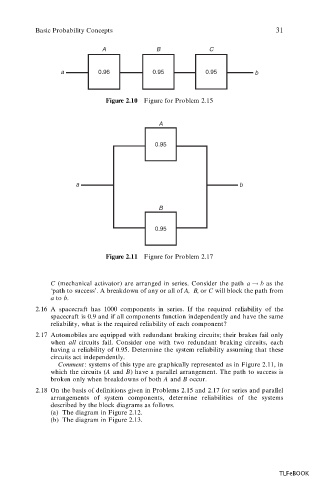
A B C
a 0.96 0.95 0.95 b
Figure 2.10 Figure for Problem 2.15
A
0.95
a b
B
0.95
Figure 2.11 Figure for Problem 2.17
C (mechanical activator) are arranged in series. Consider the path a ! b as the
‘path to success’. A breakdown of any or all of A, B, or C will block the path from
a to b.
2.16 A spacecraft has 1000 components in series. If the required reliability of the
spacecraft is 0.9 and if all components function independently and have the same
reliability, what is the required reliability of each component?
2.17 Automobiles are equipped with redundant braking circuits; their brakes fail only
when all circuits fail. Consider one with two redundant braking circuits, each
having a reliability of 0.95. Determine the system reliability assuming that these
circuits act independently.
Comment : systems of this type are graphically represented as in Figure 2.11, in
which the circuits (A and B) have a parallel arrangement. The path to success is
broken only when breakdowns of both A and B occur.
2.18 On the basis of definitions given in Problems 2.15 and 2.17 for series and parallel
arrangements of system components, determine reliabilities of the systems
described by the block diagrams as follows.
(a) The diagram in Figure 2.12.
(b) The diagram in Figure 2.13.
TLFeBOOK