Page 372 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 372
NATURAL WATER INFLUX 307
EXERCISE 9.1 APPLICATION OF THE CONSTANT TERMINAL PRESSURE
SOLUTION
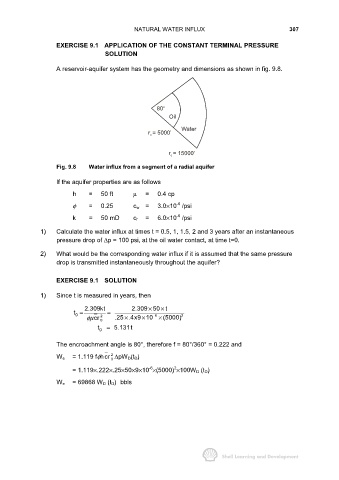
A reservoir-aquifer system has the geometry and dimensions as shown in fig. 9.8.
80 O
Oil
Water
r = 5000’
o
r = 15000’
e
Fig. 9.8 Water influx from a segment of a radial aquifer
If the aquifer properties are as follows
h = 50 ft µ = 0.4 cp
-6
φ = 0.25 c w = 3.0×10 /psi
-6
k = 50 mD c f = 6.0×10 /psi
1) Calculate the water influx at times t = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 and 3 years after an instantaneous
pressure drop of ∆p = 100 psi, at the oil water contact, at time t=0.
2) What would be the corresponding water influx if it is assumed that the same pressure
drop is transmitted instantaneously throughout the aquifer?
EXERCISE 9.1 SOLUTION
1) Since t is measured in years, then
2.309kt 2.309 50 t
×
×
t = = 6 2
D
−
×
×
φµ cr 2 0 .25 .4x9 10 × (5000)
t D = 5.131t
The encroachment angle is 80°, therefore f = 80°/360° = 0.222 and
2
W e = 1.119 fφhcr ∆pW D(t D)
0
2
-6
= 1.119×.222×.25×50×9×10 ×(5000) ×100W D (t D)
W e = 69868 W D (t D) bbls