Page 260 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 260
Coagulation 215
1.0
• Base exchange capacity of clay= 31.4 μm/L Motor
• Clay concentration=286 mg/L
0.5
Shaft guide
0.0 Cylinder
Mobility (μm/s/V/cm) –0.5 Sample in Sample out
–1.0
–1.5
–2.0 Electrode
Piston
–2.5
–3.0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Alum dosage (mg/L)
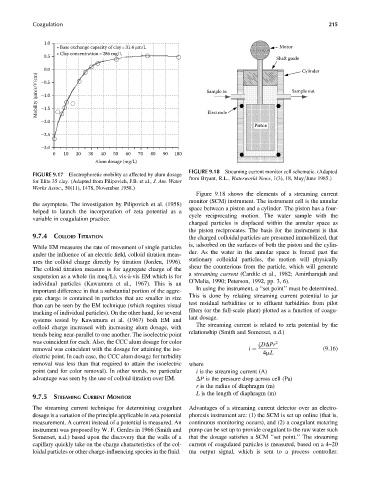
FIGURE 9.18 Streaming current monitor cell schematic. (Adapted
FIGURE 9.17 Electrophoretic mobility as affected by alum dosage
for Illite 35 clay. (Adapted from Pilipovich, J.B. et al., J. Am. Water from Bryant, R.L., Waterworld News, 1(3), 18, May=June 1985.)
Works Assoc., 50(11), 1478, November 1958.)
Figure 9.18 shows the elements of a streaming current
monitor (SCM) instrument. The instrument cell is the annular
the asymptote. The investigation by Pilipovich et al. (1958)
space between a piston and a cylinder. The piston has a four-
helped to launch the incorporation of zeta potential as a
cycle reciprocating motion. The water sample with the
variable in coagulation practice.
charged particles is displaced within the annular space as
the piston reciprocates. The basis for the instrument is that
9.7.4 COLLOID TITRATION the charged colloidal particles are presumed immobilized, that
is, adsorbed on the surfaces of both the piston and the cylin-
While EM measures the rate of movement of single particles
der. As the water in the annular space is forced past the
under the influence of an electric field, colloid titration meas-
stationary colloidal particles, the motion will physically
ures the colloid charge directly by titration (Jorden, 1996).
shear the counterions from the particle, which will generate
The colloid titration measure is for aggregate charge of the
a streaming current (Cardile et al., 1982; Amirtharajah and
suspension as a whole (in meq=L), vis-à-vis EM which is for
O’Melia, 1990; Peterson, 1992, pp. 3, 6).
individual particles (Kawamura et al., 1967). This is an
In using the instrument, a ‘‘set point’’ must be determined.
important difference in that a substantial portion of the aggre-
This is done by relating streaming current potential to jar
gate charge is contained in particles that are smaller in size
test residual turbidities or to effluent turbidities from pilot
than can be seen by the EM technique (which requires visual
filters (or the full-scale plant) plotted as a function of coagu-
tracking of individual particles). On the other hand, for several
lant dosage.
systems tested by Kawamura et al. (1967) both EM and
The streaming current is related to zeta potential by the
colloid charge increased with increasing alum dosage, with
relationship (Smith and Somerset, n.d.)
trends being near-parallel to one another. The isoelectric point
was coincident for each. Also, the CCC alum dosage for color 2
zDDPr
removal was coincident with the dosage for attaining the iso- i ¼ (9:16)
4mL
electric point. In each case, the CCC alum dosage for turbidity
removal was less than that required to attain the isoelectric where
point (and for color removal). In other words, no particular i is the streaming current (A)
advantage was seen by the use of colloid titration over EM. DP is the pressure drop across cell (Pa)
r is the radius of diaphragm (m)
L is the length of diaphragm (m)
9.7.5 STREAMING CURRENT MONITOR
The streaming current technique for determining coagulant Advantages of a streaming current detector over an electro-
dosage is a variation of the principle applicable in zeta potential phoresis instrument are: (1) the SCM is set up online (that is,
measurement. A current instead of a potential is measured. An continuous monitoring occurs), and (2) a coagulant metering
instrument was proposed by W. F. Gerdes in 1966 (Smith and pump can be set up to provide coagulant to the raw water such
Somerset, n.d.) based upon the discovery that the walls of a that the dosage satisfies a SCM ‘‘set point.’’ The streaming
capillary quickly take on the charge characteristics of the col- current of coagulated particles is measured, based on a 4–20
loidal particles or other charge-influencing species in the fluid. ma output signal, which is sent to a process controller.