Page 563 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 563
518 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
CH —CH —CH —CH —CH —CH —CH —CH —CH —CH —CH —CH—
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
SO H SO 3 H SO 3 H SO 3 H
3
CH — CH —CH — CH — CH — CH — CH —CH —CH —CH —
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
SO H SO 3 H
3
CH — CH —CH — CH — CH —CH —CH 2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Styrene
SO H SO H
3
3
CH — CH — CH — CH —
2
2
2
2
–
SO 3 functional group DVB
+
H counterion
cross-link
—CH —CH —
2
2
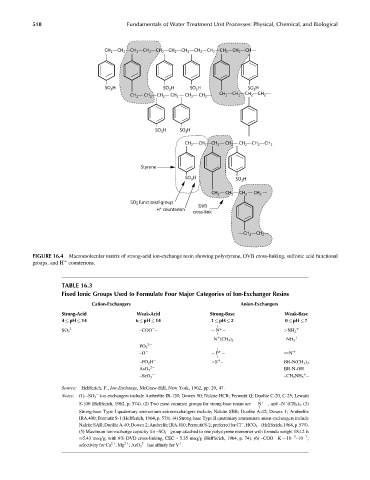
FIGURE 16.4 Macromolecular matrix of strong-acid ion-exchange resin showing polystyrene, DVB cross-linking, sulfonic acid functional
groups, and H counterions.
þ
TABLE 16.3
Fixed Ionic Groups Used to Formulate Four Major Categories of Ion-Exchanger Resins
Cation-Exchangers Anion-Exchangers
Strong-Acid Weak-Acid Strong-Base Weak-Base
4 pH 14 6 pH 14 1 pH 2 0 pH 7
2
SO 3 –COO – þ >NH 2 þ
N
þ þ
–N (CH 3 ) 3 –NH 3
2
PO 3
–O þ N þ
P
–PO 2 H >S – BR-N(CH 3 ) 3
þ
2 BR-N-OH
AsO 3
–CH 2 NH 3 –
þ
–SeO 3
Source: Helfferich, F., Ion-Exchange, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1962, pp. 29, 47.
Notes: (1) –SO 3 ion-exchangers include Amberlite IR-120; Dowex 50; Nalcite HCR; Permutit Q; Duolite C-20, C-25; Lewatit
S-100 (Helfferich, 1962, p. 574). (2) Two most common groups for strong-base resins are N ,and –N (CH 3 ) 3 .(3)
þ
þ
Strong-base Type I quaternary ammonium anion-exchangers include; Nalcite SBR; Duolite A-42; Dowex 1; Amberlite
IRA.400; Permutit S-1 (Helfferich, 1964, p. 578). (4) Strong-base Type II quaternary ammonium anion-exchangers include
NalciteSAR;DuoliteA-40;Dowex2;AmberliteIRA.410;PermutitS-2;preferredforCl ,HCO 3 (Helfferich,1964,p.579).
(5) Maximum ion-exchange capacity for –SO 3 group attached to one polystyrene monomer with formula weight 184.2 is
5
7
5.43 meq=g; with 8% DVD cross-linking, CEC ¼ 5.35 meq=g (Helfferich, 1964, p. 74). (6) –COO K ¼ 10 –10 ;
þ
2þ 2þ 2 has affinity for V .
selectivity for Ca ,Mg ;AsO 3