Page 40 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 40
30 GasPurijication
PG = gas density, lb/cu ft
K, = empirical constant
This equation was originally proposed by Souders and Brown (1934), on the basis of an
analysis of the frictional upward drag of the moving gas stream upon suspended liquid droplets.
A number of other factors such as plate design and spacing have been found to af€ect en&
ment; however, equation 1-22 is still widely used as an empirical expression by adjusting to
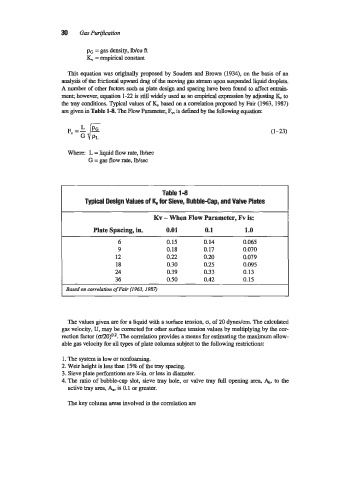
the tray conditions. Typical values of & based on a correlation proposed by Fair (1963, 1987)
are given in Table 1-8. The Flow Parameter, F,, is defd by the following equation:
(1-23)
Where: L = liquid flow rate, lb/sec
G = gas flow rate, lb/sec
Table 1-8
Typical Design Values of for Sieve, Bubble-Cap, and Valve Plates
Kv - When Flow Parameter, Fv is:
Plate Spacing, in. 0.01 0.1 1.0
6 0.15 0.14 0.065
9 0.18 0.17 0.070
12 0.22 0.20 0.079
18 0.30 0.25 0.095
24 0.39 0.33 0.13
36 0.50 0.42 0.15
Based on correlation ofFair (1963.1987)
The values given are for a liquid with a surface tension, 0, of 20 dynes/cm. The calculated
gas velocity, U, may be corrected for other surface tension values by multiplying by the cor-
rection factor (O/~O)O.~. The correlation provides a means for estimating the maximum dow-
able gas velocity for all types of plate columns subject to the following restrictions:
1. The system is low or nonfoaming.
2. Weir height is less than 15% of the tray spacing.
3. Sieve plate perforations are %-in. or less in diameter.
to
4. The ratio of bubblecap slot, sieve tray hole, or valve tray full opening area, 4, the
active tray area, A,, is 0.1 or greater.
The key column areas involved in the correlation are