Page 183 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 183
Effect of Gas Wettability on Capillaries CHAPTER 5 167
4. Gas wettability of the quartz slide surface was used to characterize gas
wettability of the inner wall surface of the capillary of this sample
group, and was appropriately labeled.
5. Capillaries of different gas wettability were placed under the microscope
to conduct a quasistatic (displacing speed 0.3 mL/h) water-displacing-
gas visualization experiment.
6. The displacement front during water-displacing-gas process was ana-
lyzed with graphic processing software.
5.1.1.3 EXPERIMENT RESULT AND DISCUSSION
5.1.1.3.1 Quantitative Evaluation of Gas Wettability of Straight
Capillary Wall Surface
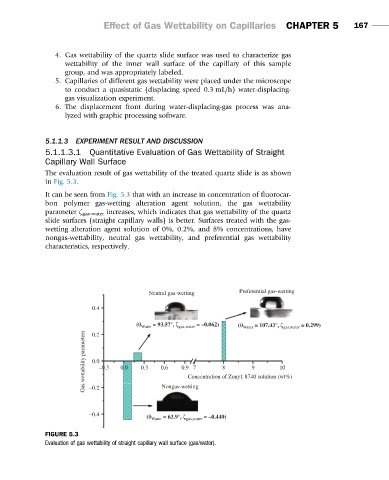
The evaluation result of gas wettability of the treated quartz slide is as shown
in Fig. 5.3.
It can be seen from Fig. 5.3 that with an increase in concentration of fluorocar-
bon polymer gas-wetting alteration agent solution, the gas wettability
parameter ζ gas-water increases, which indicates that gas wettability of the quartz
slide surfaces (straight capillary walls) is better. Surfaces treated with the gas-
wetting alteration agent solution of 0%, 0.2%, and 8% concentrations, have
nongas-wettability, neutral gas wettability, and preferential gas wettability
characteristics, respectively.
Neutral gas-wetting Preferential gas-wetting
0.4
= 93.57°, ζ = –0.062) (θ = 107.43°, ζ
(θ Water gas,water Water gas,water = 0.299)
Gas wettability parameters 0.0 –0.3 0.0 0.3 0.6 0.9 7 8 9 10
0.2
Concentration of Zony1 8740 solution (wt%)
Nongas-wetting
–0.2
–0.4 = 63.9°, ζ
(θ Water gas,water = –0.440)
FIGURE 5.3
Evaluation of gas wettability of straight capillary wall surface (gas/water).