Page 187 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 187
Effect of Gas Wettability on Capillaries CHAPTER 5 171
180 (θ = 152.48˚) (θ = 131.21˚) (θ = 126.30˚)
gas
gas
gas
160
140
Gas contact angle (˚) 100
120
80
60
40
20
0
0 2 6 7 8 9
Mass concentration of Zonyl 8740 solution (%)
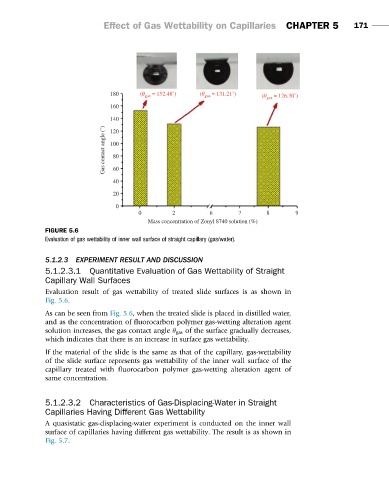
FIGURE 5.6
Evaluation of gas wettability of inner wall surface of straight capillary (gas/water).
5.1.2.3 EXPERIMENT RESULT AND DISCUSSION
5.1.2.3.1 Quantitative Evaluation of Gas Wettability of Straight
Capillary Wall Surfaces
Evaluation result of gas wettability of treated slide surfaces is as shown in
Fig. 5.6.
As can be seen from Fig. 5.6, when the treated slide is placed in distilled water,
and as the concentration of fluorocarbon polymer gas-wetting alteration agent
solution increases, the gas contact angle θ gas of the surface gradually decreases,
which indicates that there is an increase in surface gas wettability.
If the material of the slide is the same as that of the capillary, gas-wettability
of the slide surface represents gas wettability of the inner wall surface of the
capillary treated with fluorocarbon polymer gas-wetting alteration agent of
same concentration.
5.1.2.3.2 Characteristics of Gas-Displacing-Water in Straight
Capillaries Having Different Gas Wettability
A quasistatic gas-displacing-water experiment is conducted on the inner wall
surface of capillaries having different gas wettability. The result is as shown in
Fig. 5.7.