Page 191 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 191
Effect of Gas Wettability on Capillaries CHAPTER 5 175
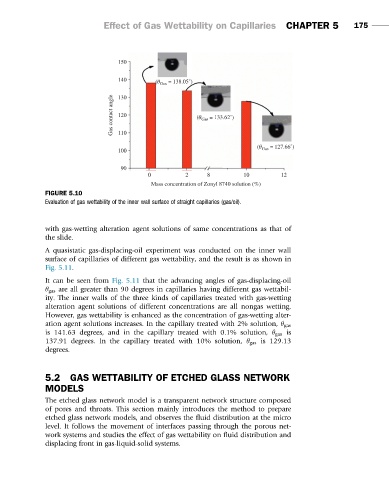
150
140
(θ Gas = 138.05˚)
Gas contact angle 120 (θ Gas = 133.62˚)
130
110
(θ = 127.66˚)
100 Gas
90
0 2 8 10 12
Mass concentration of Zonyl 8740 solution (%)
FIGURE 5.10
Evaluation of gas wettability of the inner wall surface of straight capillaries (gas/oil).
with gas-wetting alteration agent solutions of same concentrations as that of
the slide.
A quasistatic gas-displacing-oil experiment was conducted on the inner wall
surface of capillaries of different gas wettability, and the result is as shown in
Fig. 5.11.
It can be seen from Fig. 5.11 that the advancing angles of gas-displacing-oil
θ gas are all greater than 90 degrees in capillaries having different gas wettabil-
ity. The inner walls of the three kinds of capillaries treated with gas-wetting
alteration agent solutions of different concentrations are all nongas wetting.
However, gas wettability is enhanced as the concentration of gas-wetting alter-
ation agent solutions increases. In the capillary treated with 2% solution, θ gas
is 141.63 degrees, and in the capillary treated with 0.1% solution, θ gas is
137.91 degrees. In the capillary treated with 10% solution, θ gas is 129.13
degrees.
5.2 GAS WETTABILITY OF ETCHED GLASS NETWORK
MODELS
The etched glass network model is a transparent network structure composed
of pores and throats. This section mainly introduces the method to prepare
etched glass network models, and observes the fluid distribution at the micro
level. It follows the movement of interfaces passing through the porous net-
work systems and studies the effect of gas wettability on fluid distribution and
displacing front in gas-liquid-solid systems.