Page 185 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 185
Effect of Gas Wettability on Capillaries CHAPTER 5 169
5.1.2 Gas-Displacing-Oil in Capillary
5.1.2.1 EXPERIMENT THEORY
5.1.2.1.1 Evaluation of Gas Wettability of Single-straight
Capillaries
When single-straight capillaries are treated with fluorocarbon polymer gas-
wetting alteration agent solutions of different concentrations, they featured dif-
ferent gas wettability. To evaluate gas wettability of the inner wall surfaces of
capillaries intuitively and accurately, the bubble capture method was selected
as the evaluation method for gas wettability along with the gas-displacing-
water process in quasistatic conditions, and this is due to the fact that the gas
wettability process evaluated by the bubble capture method forms a three-
phase boundary on solid/water interface with air. It is similar to the
gas-displacing-water process under quasistatic conditions. Similar to the
experimental process of water-displacing-gas in single-straight capillaries,
the gas wettability of quartz slide surfaces treated with a gas-wetting alteration
agent solution of the same concentration is characteristic of the gas wettability
of the inner wall surface of the capillary.
5.1.2.1.2 Gas-Displacing-Water Experiment in Straight
Capillaries Having Different Gas Wettability
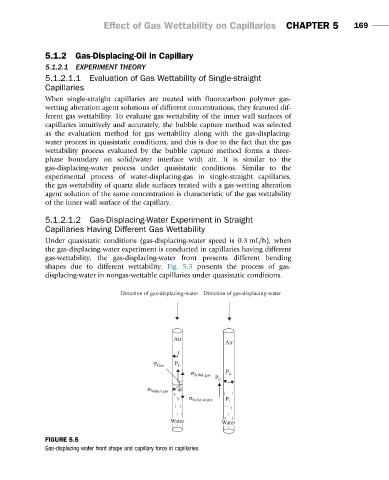
Under quasistatic conditions (gas-displacing-water speed is 0.3 mL/h), when
the gas-displacing-water experiment is conducted in capillaries having different
gas-wettability, the gas-displacing-water front presents different bending
shapes due to different wettability. Fig. 5.5 presents the process of gas-
displacing-water in nongas-wettable capillaries under quasistatic conditions.
Direction of gas-displacing-water Direction of gas-displacing-water
Air
Air
r
σ Gas P C
σ Solid-gas P 2
P C
σ Water-gas θ
σ Solid-water P 1
Water Water
FIGURE 5.5
Gas-displacing water front shape and capillary force in capillaries.