Page 251 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 251
Application of Gas Wettability CHAPTER 6 235
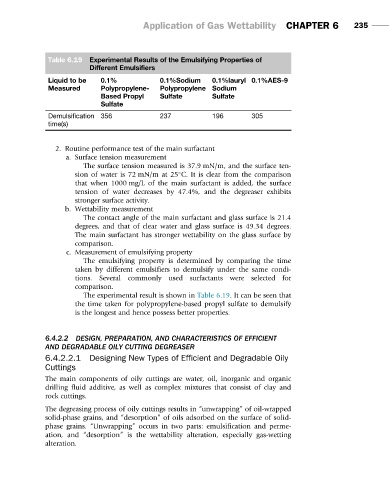
Table 6.19 Experimental Results of the Emulsifying Properties of
Different Emulsifiers
Liquid to be 0.1% 0.1%Sodium 0.1%lauryl 0.1%AES-9
Measured Polypropylene- Polypropylene Sodium
Based Propyl Sulfate Sulfate
Sulfate
Demulsification 356 237 196 305
time(s)
2. Routine performance test of the main surfactant
a. Surface tension measurement
The surface tension measured is 37.9 mN/m, and the surface ten-
sion of water is 72 mN/m at 25 C. It is clear from the comparison
that when 1000 mg/L of the main surfactant is added, the surface
tension of water decreases by 47.4%, and the degreaser exhibits
stronger surface activity.
b. Wettability measurement
The contact angle of the main surfactant and glass surface is 21.4
degrees, and that of clear water and glass surface is 49.34 degrees.
The main surfactant has stronger wettability on the glass surface by
comparison.
c. Measurement of emulsifying property
The emulsifying property is determined by comparing the time
taken by different emulsifiers to demulsify under the same condi-
tions. Several commonly used surfactants were selected for
comparison.
The experimental result is shown in Table 6.19. It can be seen that
the time taken for polypropylene-based propyl sulfate to demulsify
is the longest and hence possess better properties.
6.4.2.2 DESIGN, PREPARATION, AND CHARACTERISTICS OF EFFICIENT
AND DEGRADABLE OILY CUTTING DEGREASER
6.4.2.2.1 Designing New Types of Efficient and Degradable Oily
Cuttings
The main components of oily cuttings are water, oil, inorganic and organic
drilling fluid additive, as well as complex mixtures that consist of clay and
rock cuttings.
The degreasing process of oily cuttings results in “unwrapping” of oil-wrapped
solid-phase grains, and “desorption” of oils adsorbed on the surface of solid-
phase grains. “Unwrapping” occurs in two parts: emulsification and perme-
ation, and “desorption” is the wettability alteration, especially gas-wetting
alteration.