Page 96 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 96
80 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
2.4.5 Wetting Situation of Gas-wetting Rock Sample
Surfaces Caused by Different Liquids
1. Experimental Materials
Experimental reagent: NaCl, n-decane, n-C5, n-C6, n-C7, n-C10,
methyl alcohol, ethylalcohol, isopropyl alcohol, and ethylene glycol.
Experimental apparatus: contact angle meter, beaker, glass rod, coarse
sandpaper, and fine sandpaper.
2. Experimental Method
a. NaCl solutions of different concentrations are prepared and then
allowed to drip on the surface of gas-wetting cores. The wetting
angles of gas-wetting rock sample surfaces caused by NaCl of differ-
ent concentrations are then measured.
b. Alkane with different carbon chain length is allowed to drip on the
surface of gas-wetting cores. Contact angle method is used to mea-
sure the contact angle on core surface, and wettability of alkane on
the gas-wetting core surface is evaluated.
c. Various alcoholic solutions with varying concentrations (n-C5, n-C6,
n-C7, n-C10) are allowed to drip on the surface of gas-wetting cores.
Contact angle method is used to measure the contact angle on the
core surface, and wettability of alkane on the gas-wetting core surface
is evaluated.
2.4.5.1 WETTABILITY OF SURFACES OF GAS-WETTING ROCK SAMPLES
CAUSED BY NACL SOLUTIONS OF DIFFERENT CONCENTRATIONS
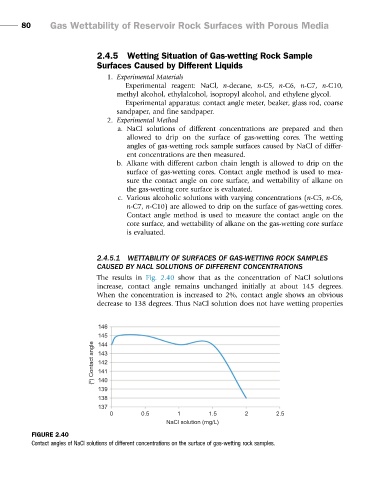
The results in Fig. 2.40 show that as the concentration of NaCl solutions
increase, contact angle remains unchanged initially at about 145 degrees.
When the concentration is increased to 2%, contact angle shows an obvious
decrease to 138 degrees. Thus NaCl solution does not have wetting properties
146
145
(º) Contact angle 143
144
142
141
140
139
138
137
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
NaCl solution (mg/L)
FIGURE 2.40
Contact angles of NaCl solutions of different concentrations on the surface of gas-wetting rock samples.