Page 98 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 98
82 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
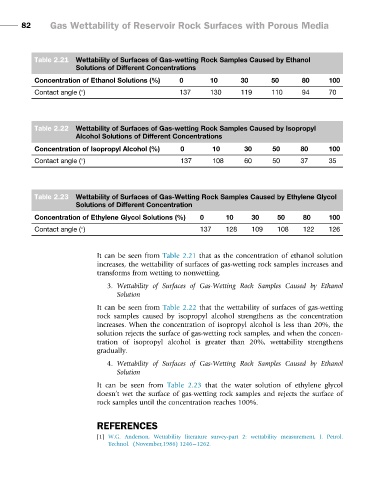
Table 2.21 Wettability of Surfaces of Gas-wetting Rock Samples Caused by Ethanol
Solutions of Different Concentrations
Concentration of Ethanol Solutions (%) 0 10 30 50 80 100
Contact angle ( ) 137 130 119 110 94 70
Table 2.22 Wettability of Surfaces of Gas-wetting Rock Samples Caused by Isopropyl
Alcohol Solutions of Different Concentrations
Concentration of Isopropyl Alcohol (%) 0 10 30 50 80 100
Contact angle ( ) 137 108 60 50 37 35
Table 2.23 Wettability of Surfaces of Gas-Wetting Rock Samples Caused by Ethylene Glycol
Solutions of Different Concentration
Concentration of Ethylene Glycol Solutions (%) 0 10 30 50 80 100
Contact angle ( ) 137 128 109 108 122 126
It can be seen from Table 2.21 that as the concentration of ethanol solution
increases, the wettability of surfaces of gas-wetting rock samples increases and
transforms from wetting to nonwetting.
3. Wettability of Surfaces of Gas-Wetting Rock Samples Caused by Ethanol
Solution
It can be seen from Table 2.22 that the wettability of surfaces of gas-wetting
rock samples caused by isopropyl alcohol strengthens as the concentration
increases. When the concentration of isopropyl alcohol is less than 20%, the
solution rejects the surface of gas-wetting rock samples, and when the concen-
tration of isopropyl alcohol is greater than 20%, wettability strengthens
gradually.
4. Wettability of Surfaces of Gas-Wetting Rock Samples Caused by Ethanol
Solution
It can be seen from Table 2.23 that the water solution of ethylene glycol
doesn’t wet the surface of gas-wetting rock samples and rejects the surface of
rock samples until the concentration reaches 100%.
REFERENCES
[1] W.G. Anderson, Wettability literature survey-part 2: wettability measurement, J. Petrol.
Technol. (November,1986) 1246 1262.