Page 323 - gas transport in porous media
P. 323
322
1400
1200 Tartre
Concentrations (in ppm) 1000
800
600
400 Purge is
stopped
200
0
0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3
Time (in minutes)
1400
1200
1000
Concentrations (in ppm) 800
600
400 Purge is
stopped
200
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Time (in minutes)
1400
1200
1000
Concentrations (in ppm) 800 Purge is
stopped
600
400
200
0
0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3
Time (in minutes)
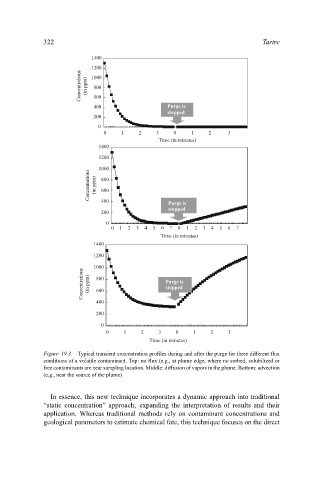
Figure 19.3. Typical transient concentration profiles during and after the purge for three different flux
conditions of a volatile contaminant. Top: no flux (e.g., at plume edge, where no sorbed, solubilized or
free contaminants are near sampling location. Middle: diffusion of vapors in the plume. Bottom: advection
(e.g., near the source of the plume)
In essence, this new technique incorporates a dynamic approach into traditional
“static concentration” approach, expanding the interpretation of results and their
application. Whereas traditional methods rely on contaminant concentrations and
geological parameters to estimate chemical fate, this technique focuses on the direct