Page 47 - gas transport in porous media
P. 47
40
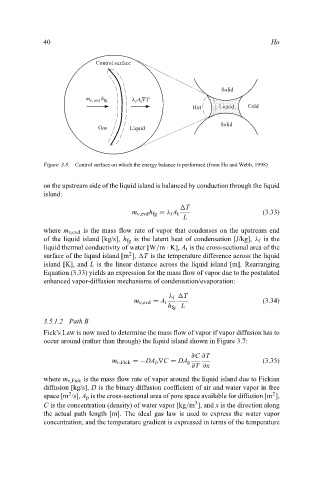
Control surface Ho
Solid
m v, evd h fg λ l A t ∇T
Hot Liquid Cold
Solid
Gas Liquid
Figure 3.8. Control surface on which the energy balance is performed (from Ho and Webb, 1998)
on the upstream side of the liquid island is balanced by conduction through the liquid
island:
T
m v,evd h fg = λ l A t (3.33)
L
where m v,evd is the mass flow rate of vapor that condenses on the upstream end
of the liquid island [kg/s], h fg is the latent heat of condensation [J/kg], λ l is the
liquid thermal conductivity of water [W/m · K], A t is the cross-sectional area of the
2
surface of the liquid island [m ], T is the temperature difference across the liquid
island [K], and L is the linear distance across the liquid island [m]. Rearranging
Equation (3.33) yields an expression for the mass flow of vapor due to the postulated
enhanced vapor-diffusion mechanisms of condensation/evaporation:
λ l T
m v,evd = A t (3.34)
h fg L
3.5.1.2 Path B
Fick’s Law is now used to determine the mass flow of vapor if vapor diffusion has to
occur around (rather than through) the liquid island shown in Figure 3.7:
∂C ∂T
m v,Fick =−DA p ∇C = DA p (3.35)
∂T ∂x
where m v,Fick is the mass flow rate of vapor around the liquid island due to Fickian
diffusion [kg/s], D is the binary diffusion coefficient of air and water vapor in free
2
2
space [m /s], A p is the cross-sectional area of pore space available for diffusion [m ],
3
C is the concentration (density) of water vapor [kg/m ], and x is the direction along
the actual path length [m]. The ideal gas law is used to express the water vapor
concentration, and the temperature gradient is expressed in terms of the temperature