Page 57 - gas transport in porous media
P. 57
50
300
0% Relative humidity Ong
40% Relative humidity
Mass sorbed / mass sorbent (mg/g) 200
250
70% Relative humidity
150
100
50
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
Relative vapor pressure of trichloroethylene (P/P )
o
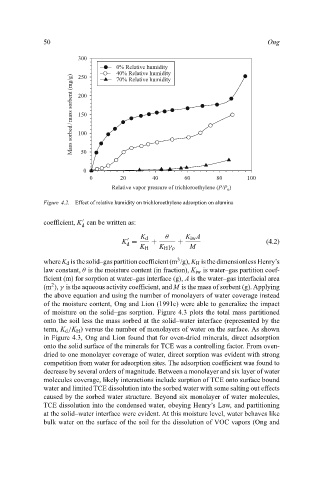
Figure 4.2. Effect of relative humidity on trichloroethylene adsorption on alumina
coefficient, K can be written as:
d
K d θ K iw A
K = + + (4.2)
d
K H K H γ ρ M
3
whereK d isthesolid–gaspartitioncoefficient(m /g), K H isthedimensionlessHenry’s
law constant, θ is the moisture content (in fraction), K iw is water–gas partition coef-
ficient (m) for sorption at water–gas interface (g), A is the water–gas interfacial area
2
(m ), γ is the aqueous activity coefficient, and M is the mass of sorbent (g). Applying
the above equation and using the number of monolayers of water coverage instead
of the moisture content, Ong and Lion (1991c) were able to generalize the impact
of moisture on the solid–gas sorption. Figure 4.3 plots the total mass partitioned
onto the soil less the mass sorbed at the solid–water interface (represented by the
term, K d /K H ) versus the number of monolayers of water on the surface. As shown
in Figure 4.3, Ong and Lion found that for oven-dried minerals, direct adsorption
onto the solid surface of the minerals for TCE was a controlling factor. From oven-
dried to one monolayer coverage of water, direct sorption was evident with strong
competition from water for adsorption sites. The adsorption coefficient was found to
decrease by several orders of magnitude. Between a monolayer and six layer of water
molecules coverage, likely interactions include sorption of TCE onto surface bound
water and limited TCE dissolution into the sorbed water with some salting out effects
caused by the sorbed water structure. Beyond six monolayer of water molecules,
TCE dissolution into the condensed water, obeying Henry’s Law, and partitioning
at the solid–water interface were evident. At this moisture level, water behaves like
bulk water on the surface of the soil for the dissolution of VOC vapors (Ong and