Page 70 - Geochemical Remote Sensing of The Sub-Surface
P. 70
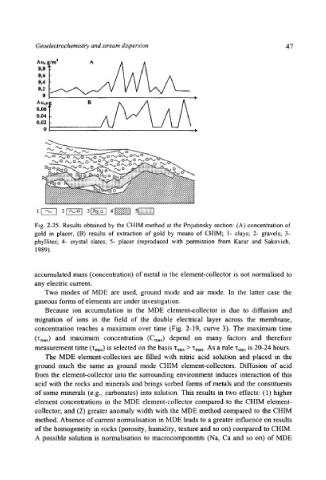
Geoelectrochemistry and stream dispersion 47
/ku~
0,8
0,6
0,4
0,2
0
B
0.06 "[
0.04 ~-
0"020 I.
Fig. 2-25. Results obtained by the CHIM method at the Prijutinsky section: (A) concentration of
gold in placer, (B) results of extraction of gold by means of CHIM; 1- clays; 2- gravels; 3-
phyllites; 4- crystal slates; 5- placer (reproduced with permission from Karar and Sakovich,
1989).
accumulated mass (concentration) of metal in the element-collector is not normalised to
any electric current.
Two modes of MDE are used, ground mode and air mode. In the latter case the
gaseous forms of elements are under investigation.
Because ion accumulation in the MDE element-collector is due to diffusion and
migration of ions in the field of the double electrical layer across the membrane,
concentration reaches a maximum over time (Fig. 2-19, curve 3). The maximum time
(Xmax) and maximum concentration (Cmax) depend on many factors and therefore
measurement time (Xmes) is selected on the basis "lTme s > Xma x. As a rule "l~me s is 20-24 hours.
The MDE element-collectors are filled with nitric acid solution and placed in the
ground much the same as ground mode CHIM element-collectors. Diffusion of acid
from the element-collector into the surrounding environment induces interaction of this
acid with the rocks and minerals and brings sorbed forms of metals and the constituents
of some minerals (e.g., carbonates) into solution. This results in two effects: (1) higher
element concentrations in the MDE element-collector compared to the CHIM element-
collector; and (2) greater anomaly width with the MDE method compared to the CHIM
method. Absence of current normalisation in MDE leads to a greater influence on results
of the homogeneity in rocks (porosity, humidity, texture and so on) compared to CHIM.
A possible solution is normalisation to macrocomponents (Na, Ca and so on) of MDE