Page 184 - Geochemistry of Oil Field Waters
P. 184
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 171
Ionic radii
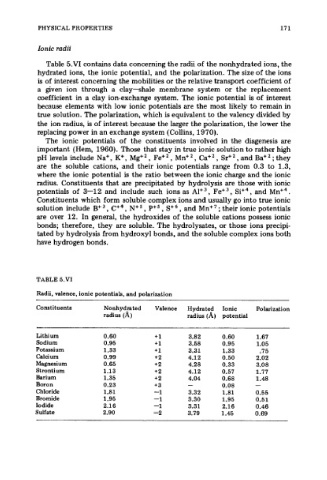
Table 5.VI contains data concerning the radii of the nonhydrated ions, the
hydrated ions, the ionic potential, and the polarization. The size of the ions
is of interest concerning the mobilities or the relative transport coefficient of
a given ion through a clayshale membrane system or the replacement
coefficient in a clay ion-exchange system. The ionic potential is of interest
because elements with low ionic potentials are the most likely to remain in
true solution. The polarization, which is equivalent to the valency divided by
the ion radius, is of interest because the larger the polarization, the lower the
replacing power in an exchange system (Collins, 1970).
The ionic potentials of the constituents involved in the diagenesis are
important (Hem, 1960). Those that stay in true ionic solution to rather high
pH levels include Na+, K+, Mg+’, Fe+’, Mn+’, Ca+’, Sr+*, and Ba+’ ; they
are the soluble cations, and their ionic potentials range from 0.3 to 1.3,
where the ionic potential is the ratio between the ionic charge and the ionic
radius. Constituents that are precipitated by hydrolysis are those with ionic
potentials of 3-12 and include such ions as AP3, Fe+3, SP4, and MrP4.
Constituents which form soluble complex ions and usually go into true ionic
solution include B+3, C4, N+5, P+’, S6, and Mn+’ ; their ionic potentials
are over 12. In general, the hydroxides of the soluble cations possess ionic
bonds; therefore, they are soluble. The hydrolysates, or those ions precipi-
tated by hydrolysis from hydroxyl bonds, and the soluble complex ions both
have hydrogen bonds.
TABLE 5.VI
Radii, valence, ionic potentials, and polarization
Constituents Nonhydrated Valence Hydrated Ionic Polarization
radius (A) radius (A) potential
Lithium 0.60 +1 3.82 0.60 1.67
Sodium 0.95 +1 3.58 0.95 1.05
Potassium 1.33 +1 3.31 1.33 .75
Calcium 0.99 +2 4.12 0.50 2.02
Magnesium 0.65 +2 4.28 0.33 3.08
Strontium 1.13 +2 4.12 0.57 1.77
Barium 1.35 +2 4.04 0.68 1.48
Boron 0.23 +3 - 0.08 -
Chloride 1.81 -1 3.32 1.81 0.55
Bromide 1.95 -1 3.30 1.95 0.51
Iodide 2.16 -1 3.31 2.16 0.46
Sulfate 2.90 -2 3.79 1.45 0.69