Page 175 - Geometric Modeling and Algebraic Geometry
P. 175
9 Intersecting Biquadratic Patches 177
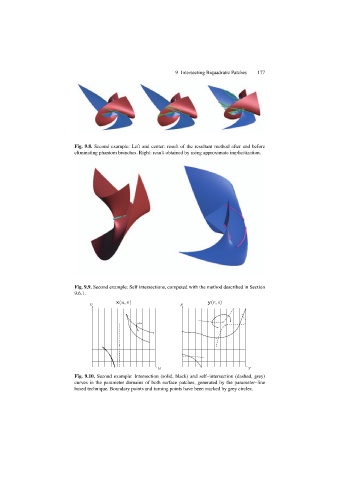
Fig. 9.8. Second example: Left and center: result of the resultant method after and before
eliminating phantom branches. Right: result obtained by using approximate implicitization.
Fig. 9.9. Second example: Self intersections, computed with the method described in Section
9.6.1.
x(u, v) y(r, s)
v s
u r
Fig. 9.10. Second example: Intersection (solid, black) and self–intersection (dashed, grey)
curves in the parameter domains of both surface patches, generated by the parameter–line
based technique. Boundary points and turning points have been marked by grey circles.