Page 218 - Geothermal Energy Renewable Energy and The Environment
P. 218
206 Geothermal Energy: Renewable Energy and the Environment
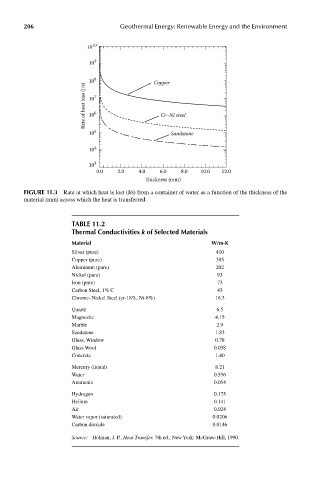
10 10
10 9 8 Copper
Rate of heat loss (J/s) 10 7 6 Cr–Ni steel
10
10
10 5 Sandstone
10 4
10 3
0.0 2.0 4.0 6. 0 8 .0 10.0 12.0
Thickness (mm)
FIGUre 11.3 Rate at which heat is lost (J/s) from a container of water as a function of the thickness of the
material (mm) across which the heat is transferred.
Table 11.2
Thermal conductivities k of selected materials
material w/m-k
Silver (pure) 410
Copper (pure) 385
Aluminum (pure) 202
Nickel (pure) 93
Iron (pure) 73
Carbon Steel, 1% C 43
Chrome–Nickel Steel (cr-18%, Ni-8%) 16.3
Quartz 6.5
Magnesite 4.15
Marble 2.9
Sandstone 1.83
Glass, Window 0.78
Glass Wool 0.038
Concrete 1.40
Mercury (liquid) 8.21
Water 0.556
Ammonia 0.054
Hydrogen 0.175
Helium 0.141
Air 0.024
Water vapor (saturated) 0.0206
Carbon dioxide 0.0146
Source: Holman, J. P., Heat Transfer, 7th ed., New York: McGraw-Hill, 1990.