Page 86 - Geothermal Energy Renewable Energy and The Environment
P. 86
Chemistry of Geothermal Fluids 71
H H H
O O O
H H H
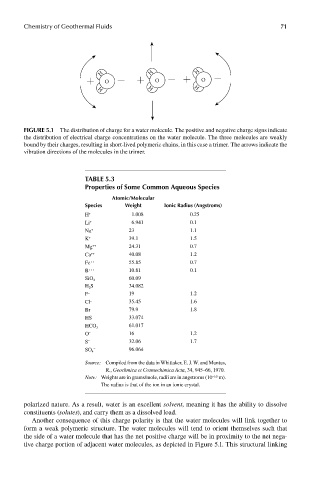
FIGUre 5.1 The distribution of charge for a water molecule. The positive and negative charge signs indicate
the distribution of electrical charge concentrations on the water molecule. The three molecules are weakly
bound by their charges, resulting in short-lived polymeric chains, in this case a trimer. The arrows indicate the
vibration directions of the molecules in the trimer.
Table 5.3
properties of some common aqueous species
atomic/molecular
species weight Ionic radius (angstroms)
H + 1.008 0.25
Li + 6.941 0.1
Na + 23 1.1
K + 39.1 1.5
Mg ++ 24.31 0.7
Ca ++ 40.08 1.2
Fe ++ 55.85 0.7
B +++ 10.81 0.1
60.09
SiO 2
H 2 S 34.082
F − 19 1.2
Cl − 35.45 1.6
Br − 79.9 1.8
HS − 33.074
− 61.017
HCO 3
O − 16 1.2
S − 32.06 1.7
− 96.064
SO 4
Source: Compiled from the data in Whittaker, E. J. W. and Muntus,
R., Geochmica et Cosmochimica Acta, 34, 945–66, 1970.
Note: Weights are in grams/mole, radii are in angstroms (10 m).
−10
The radius is that of the ion in an ionic crystal.
polarized nature. As a result, water is an excellent solvent, meaning it has the ability to dissolve
constituents (solutes), and carry them as a dissolved load.
Another consequence of this charge polarity is that the water molecules will link together to
form a weak polymeric structure. The water molecules will tend to orient themselves such that
the side of a water molecule that has the net positive charge will be in proximity to the net nega-
tive charge portion of adjacent water molecules, as depicted in Figure 5.1. This structural linking