Page 286 - Global Project Management Handbook
P. 286
PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR OUTSOURCING DECISIONS 14-11
East
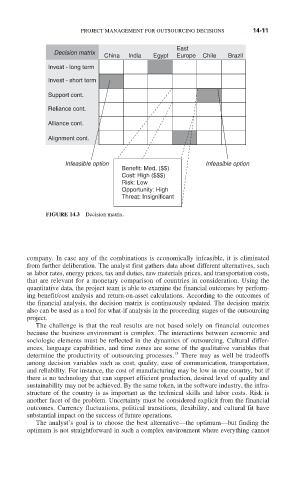
Decision matrix
China India Egypt Europe Chile Brazil
Invest - long term
Invest - short term
Support cont.
Reliance cont.
Alliance cont.
Alignment cont.
Infeasible option Infeasible option
Benefit: Med. ($$)
Cost: High ($$$)
Risk: Low
Opportunity: High
Threat: Insignificant
FIGURE 14.3 Decision matrix.
company. In case any of the combinations is economically infeasible, it is eliminated
from further deliberation. The analyst first gathers data about different alternatives, such
as labor rates, energy prices, tax and duties, raw materials prices, and transportation costs,
that are relevant for a monetary comparison of countries in consideration. Using the
quantitative data, the project team is able to examine the financial outcomes by perform-
ing benefit/cost analysis and return-on-asset calculations. According to the outcomes of
the financial analysis, the decision matrix is continuously updated. The decision matrix
also can be used as a tool for what-if analysis in the proceeding stages of the outsourcing
project.
The challenge is that the real results are not based solely on financial outcomes
because the business environment is complex. The interactions between economic and
sociologic elements must be reflected in the dynamics of outsourcing. Cultural differ-
ences, language capabilities, and time zones are some of the qualitative variables that
determine the productivity of outsourcing processes. 13 There may as well be tradeoffs
among decision variables such as cost, quality, ease of communication, transportation,
and reliability. For instance, the cost of manufacturing may be low in one country, but if
there is no technology that can support efficient production, desired level of quality and
sustainability may not be achieved. By the same token, in the software industry, the infra-
structure of the country is as important as the technical skills and labor costs. Risk is
another facet of the problem. Uncertainty must be considered explicit from the financial
outcomes. Currency fluctuations, political transitions, flexibility, and cultural fit have
substantial impact on the success of future operations.
The analyst’s goal is to choose the best alternative—the optimum—but finding the
optimum is not straightforward in such a complex environment where everything cannot