Page 287 - Global Project Management Handbook
P. 287
14-12 MANAGEMENT OF GLOBAL PROGRAMS AND PROJECTS
Sensitivity analysis
Analysis of
current Risks and
system threats
Objective Data Criteria
collection rating
Alternative Priority
system allocation
requirements
Quantitative analysis Qualitative analysis
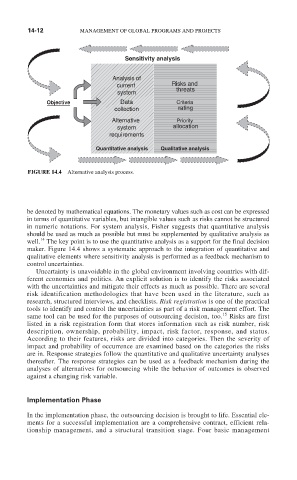
FIGURE 14.4 Alternative analysis process.
be denoted by mathematical equations. The monetary values such as cost can be expressed
in terms of quantitative variables, but intangible values such as risks cannot be structured
in numeric notations. For system analysis, Fisher suggests that quantitative analysis
should be used as much as possible but must be supplemented by qualitative analysis as
14
well. The key point is to use the quantitative analysis as a support for the final decision
maker. Figure 14.4 shows a systematic approach to the integration of quantitative and
qualitative elements where sensitivity analysis is performed as a feedback mechanism to
control uncertainties.
Uncertainty is unavoidable in the global environment involving countries with dif-
ferent economies and politics. An explicit solution is to identify the risks associated
with the uncertainties and mitigate their effects as much as possible. There are several
risk identification methodologies that have been used in the literature, such as
research, structured interviews, and checklists. Risk registration is one of the practical
tools to identify and control the uncertainties as part of a risk management effort. The
same tool can be used for the purposes of outsourcing decision, too. 15 Risks are first
listed in a risk registration form that stores information such as risk number, risk
description, ownership, probability, impact, risk factor, response, and status.
According to their features, risks are divided into categories. Then the severity of
impact and probability of occurrence are examined based on the categories the risks
are in. Response strategies follow the quantitative and qualitative uncertainty analyses
thereafter. The response strategies can be used as a feedback mechanism during the
analyses of alternatives for outsourcing while the behavior of outcomes is observed
against a changing risk variable.
Implementation Phase
In the implementation phase, the outsourcing decision is brought to life. Essential ele-
ments for a successful implementation are a comprehensive contract, efficient rela-
tionship management, and a structural transition stage. Four basic management