Page 84 - Global Project Management Handbook
P. 84
THE FUTURE OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT 3-17
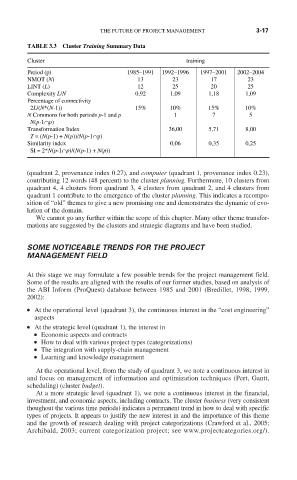
TABLE 3.3 Cluster Training Summary Data
Cluster training
Period (p) 1985–1991 1992–1996 1997–2001 2002–2004
NMOT (N) 13 23 17 23
LINT (L) 12 25 20 25
Complexity L/N 0,92 1,09 1,18 1,09
Percentage of connectivity
2L/(N*(N-1)) 15% 10% 15% 10%
N Commons for both periods p-1 and p 1 7 5
N(p-1∩p)
Transformation Index 36,00 5,71 8,00
T = (N(p-1) + N(p))/N(p-1∩p)
Similarity index 0,06 0,35 0,25
SI = 2*N(p-1∩p)/(N(p-1) + N(p))
(quadrant 2, provenance index 0.27), and computer (quadrant 1, provenance index 0.23),
contributing 12 words (48 percent) to the cluster planning. Furthermore, 10 clusters from
quadrant 4, 4 clusters from quadrant 3, 4 clusters from quadrant 2, and 4 clusters from
quadrant 1 contribute to the emergence of the cluster planning. This indicates a recompo-
sition of “old” themes to give a new promising one and demonstrates the dynamic of evo-
lution of the domain.
We cannot go any further within the scope of this chapter. Many other theme transfor-
mations are suggested by the clusters and strategic diagrams and have been studied.
SOME NOTICEABLE TRENDS FOR THE PROJECT
MANAGEMENT FIELD
At this stage we may formulate a few possible trends for the project management field.
Some of the results are aligned with the results of our former studies, based on analysis of
the ABI Inform (ProQuest) database between 1985 and 2001 (Bredillet, 1998, 1999,
2002):
● At the operational level (quadrant 3), the continuous interest in the “cost engineering”
aspects
● At the strategic level (quadrant 1), the interest in
● Economic aspects and contracts
● How to deal with various project types (categorizations)
● The integration with supply-chain management
● Learning and knowledge management
At the operational level, from the study of quadrant 3, we note a continuous interest in
and focus on management of information and optimization techniques (Pert, Gantt,
scheduling) (cluster budget).
At a more strategic level (quadrant 1), we note a continuous interest in the financial,
investment, and economic aspects, including contracts. The cluster business (very consistent
thoughout the various time periods) indicates a permanent trend in how to deal with specific
types of projects. It appears to justify the new interest in and the importance of this theme
and the growth of research dealing with project categorizations (Crawford et al., 2005;
Archibald, 2003; current categorization project; see www.projectcategories.org/).