Page 332 - Global Tectonics
P. 332
OROGENIC BELTS 315
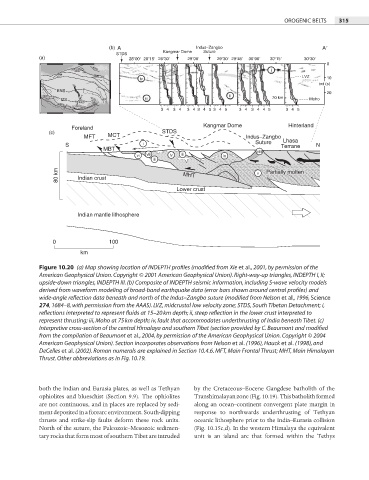
(b) A Indus–Zangbo A
STDS Kangmar Dome Suture
(a) 28 00 28 15 28 30 29 00 29 30 29 45 30 00 30 15 30 30
0
4000 4000 i
4000 4000
4000 LVZ
iv 10
twt (s)
BNS 20
4000 ii 70 km
2000 IZS 4000 4000 iii Moho
4000 4000 2000
2000 4000 2000
MTB 3 4 34 34 345 345 34 344 5 345
Foreland Kangmar Dome Hinterland
(c) MCT STDS
MFT Indus–Zangbo Lhasa
S i Suture Terrane N
MBT viii
vi vii iv iii ix
ii
80 km Indian crust MHT v Partially molten
Lower crust
Indian mantle lithosphere
0 100
km
Figure 10.20 (a) Map showing location of INDEPTH profiles (modified from Xie et al., 2001, by permission of the
American Geophysical Union. Copyright © 2001 American Geophysical Union). Right-way-up triangles, INDEPTH I, II;
upside-down triangles, INDEPTH III. (b) Composite of INDEPTH seismic information, including S-wave velocity models
derived from waveform modeling of broad-band earthquake data (error bars shown around central profiles) and
wide-angle reflection data beneath and north of the Indus–Zangbo suture (modified from Nelson et al., 1996, Science
274, 1684–8, with permission from the AAAS). LVZ, midcrustal low velocity zone; STDS, South Tibetan Detachment; i,
reflections interpreted to represent fluids at 15–20 km depth; ii, steep reflection in the lower crust interpreted to
represent thrusting; iii, Moho at 75 km depth; iv, fault that accommodates underthrusting of India beneath Tibet. (c)
Interpretive cross-section of the central Himalaya and southern Tibet (section provided by C. Beaumont and modified
from the compilation of Beaumont et al., 2004, by permission of the American Geophysical Union. Copyright © 2004
American Geophysical Union). Section incorporates observations from Nelson et al. (1996), Hauck et al. (1998), and
DeCelles et al. (2002). Roman numerals are explained in Section 10.4.6. MFT, Main Frontal Thrust; MHT, Main Himalayan
Thrust. Other abbreviations as in Fig. 10.19.
both the Indian and Eurasia plates, as well as Tethyan by the Cretaceous–Eocene Gangdese batholith of the
ophiolites and blueschist (Section 9.9). The ophiolites Transhimalayan zone (Fig. 10.19). This batholith formed
are not continuous, and in places are replaced by sedi- along an ocean–continent convergent plate margin in
ment deposited in a forearc environment. South-dipping response to northwards underthrusting of Tethyan
thrusts and strike-slip faults deform these rock units. oceanic lithosphere prior to the India–Eurasia collision
North of the suture, the Paleozoic–Mesozoic sedimen- (Fig. 10.15c,d). In the western Himalaya the equivalent
tary rocks that form most of southern Tibet are intruded unit is an island arc that formed within the Tethys